Date: November 6, 2021 | Updated: December 25, 2021 | Author: Moblie-man
The number of active subscribers of MTS suggests that this operator has the right to be on the list of the most popular cellular corporations in Russia. However, such a number of clients inevitably leads to an endless stream of questions and requests from users related to a variety of topics.
For example, subscribers are often interested in the question of how to set up mobile Internet on MTS. And today, in our article, we will try to give a comprehensive answer to this question, considering all the most common situations and configuration nuances.
How to set up MTS Internet on your phone and tablet
We need to start our conversation with the fact that the setup procedure is no different whether you are configuring a tablet computer or a smartphone. Users are often interested in different configurations for different devices, but they all have an identical appearance, because, for example, Apple tablets have the same operating system on board as Apple iPhone smartphones. The same situation is observed with Android devices: the screen diagonal is different, but the operating system is the same - Android OS.
How to set up Beeline Internet automatically
Automated receipt of configurations greatly facilitates the use of a smartphone for many subscribers, especially those who have no idea how to configure gadgets.
Beeline clients do not need to perform any additional manipulations to enable this function. The service is configured automatically.
But situations are different. Therefore, you need to know how to solve the problem with your Internet connection.
Call to a special number
If the network connection settings have been reset on your mobile phone and the access point does not function, it is recommended to re-order automatic settings from your mobile operator.
To do this, you need to dial the short free number 0880 on your device and press the call button. The provider will send configuration connection parameters via text message within a few minutes.
The subscriber will only need to save the received information and reboot the device. After this, network access will resume.
USSD request
You can also request auto settings using a special command by dialing a combination of numbers and symbols *110*181# and the call button on your smartphone.
You can directly contact the Beeline operator at 88007000611.
Official website of the operator
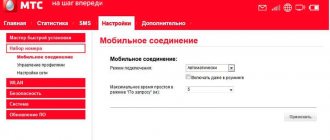
You can restore Internet access yourself through the official portal of the provider. To do this, you need to register on the website of the cellular company, gain access to your personal account, through which you can set the necessary parameters.
Procedure:
- Log in to your “Personal Account”.
- In the menu, find the “Phone Settings” section and open it.
- Enter the device model in the empty field.
- Select the sub-item “Mobile Internet”.
- If text appears on the screen stating that such a device has auto settings, you need to enter your number. Send a request.
- The parameters will be sent via SMS to the phone number specified in the application.
- You need to save them and reboot the gadget.
All of the listed methods for obtaining network connection configurations are provided by the provider free of charge.
Getting settings for mobile Internet.
Automatic settings
If you have difficulties accessing the World Wide Web or sending MMS, first of all, order automatic settings from your operator. You can do this in several ways:
- Dial the USSD command *111*2156# and then follow the instructions that will appear on the screen.
- Send a free SMS without text to number 1234 and wait for response instructions.
- Get settings by entering your phone number on the official MTS website. On the main page, find the Help tab, then go to the Mobile Internet section, and then – Order automatic settings. And also make a request in the user’s Personal Account. Find the Number Management section, and in it - Internet Assistant. On this page, go to Settings, then Internet and MMS settings. You will need to fill in the following information: - Your number to which you want to connect the Internet; — Brand and model of the device; — Settings type: Internet/WAP/SMS; — The format for receiving instructions is via SMS. After the SMS arrives on your phone and all configurations are activated, reboot the device.
Automatic adoption of innovations is the simplest and fastest way, which will not take you much time and which even a child can handle.
However, if instructions do not arrive on your device or the phone refuses to accept them, you will have to resort to manual control.
Automatic Internet setup on MTS
Moving directly to the procedure for setting up the device, let’s first note the simplest configuration method. It consists of ordering a standard preset of settings in automatic mode, thanks to which subscribers do not need to go into the settings of the gadget they are using and change them themselves. You can order automatic settings in several ways:
- In your personal account on the operator’s website.
- When calling the number 0876.
- When sending an SMS message to 1234 , the text of which will indicate “Internet” without quotes.
The settings will be received on the device in a message, after launching which you will see a notification on the device’s display asking for permission to apply the new settings. Having answered it convincingly, the parameters will be saved in the gadget, and after the “reboot” the mobile internet should function correctly and uninterruptedly.
How to configure network access manually
Handwork is also quite simple, although it may seem otherwise at first. It should be noted that the procedure for changing configurations for smartphones and tablets is the same, the only difference will be in the operating systems. So for Android phones and tablets the operating principle will be the same, but for iPad and iPhone it will be different.
Below we list the parameters that will need to be filled in during setup for users of all operating systems. Just take it and rewrite it:
- Name – MTS Internet;
- APN – internet.mts.ru;
- Username – MTS;
- Password – MTS.
Android smartphones
The instructions for setting up 4G MTS APN, common to all Android devices, look like this:
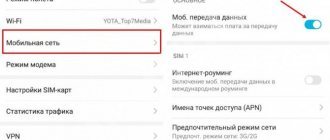
- Go to "Settings".
- Select the “Mobile networks” section.
- Go to the subsection “Setting up a SIM card”
- In the “APN access points” item, create a new point or change the values of the old one: Name – MTS internet, APN – internet.mts.ru, Login – mts, Password – mts.
You do not need to touch, fill out or change any other fields. After entering the values, the settings are saved and applied. To access the network, it is advisable to restart the phone.
How to set up MTS Internet on iPhone
Users of premium Apple technology, regardless of whether it is an iPad or an iPhone, can set it up themselves if they strictly follow the instructions below:
- Open the device settings and go to the “Cellular” section.
- Find the "Data Options" option located at the top of the menu.
- Move to the Cellular Data subcategory.
- Next, proceed to enter the appropriate parameters into the fields available in the menu. In the “Cellular Data” subcategory, you must one by one enter the parameters internet.mts.ru , mts and mts for the “APN” , “Name” and “Password” , respectively.
- Move to the next item on the page and specify the correct parameters for the operation of LTE networks. The same parameters are entered there as in the “Cellular Data” menu.
- Save the changes and restart your Apple device.
After entering these settings, mobile Internet on your iPhone or iPad will work correctly. And if you decide to “distribute” it via Wi-Fi, you will also need to enter identical values that we have already discussed earlier in the “Modem Mode” section of the device.
On Windows Phone
If your device runs on this platform, you will also need to call up the section with combinations, and then go to the “Data Transfer” menu. Here you need to find and select the “Add point” option. Next, you must specify all the values for connecting to MTS. Upon completion, you need to save the settings, and then reboot the gadget.
Important! All parameters that have to be entered manually are standard for any device; they can be found on the official website of the cellular operator (usually Name - MTS internet, APN - internet.mts.ru, Login - mts and Password mts).
In order to use the opportunity to visit Internet resources, new subscribers need to obtain the appropriate settings for their gadget. Typically, these settings come automatically, however, if this does not happen, you may need to manually enter the values. In practice, this should not pose any particular problems, since the operator has foreseen all the nuances in advance, and has also prepared detailed instructions and procedures.
On tablets
These devices run on the same operating systems as smartphones. Their access point settings are identical. The iPad is initially loaded with the necessary MTS settings.
On a modem from MTS
To access the network, modems are fully configured; no action is required from the user. To connect, you need to insert the device into a USB port. The installation of drivers and software will begin. When the process is complete, you can connect.
If the modem is universal, it may contain profiles of several operators. In this case, we leave MTS and delete all others.
If the settings section is empty, enter the data yourself:
- In the program we look for the section where new profiles are created.
- We fill it out in the same way as for smartphones.
- We write the call number *99#.
Next, you need to save it, set its status to “Default”, and you can use the Internet.
The setup is carried out according to a common standard for all devices, the parameters are always the same, only the path to them differs due to differences in models. If for some reason you cannot access the network, you should contact the service phone or the company’s showroom. Another option is . Its connection and use is free. You also need to make sure that the mobile Internet or data transfer button is in the active position - this is often the reason for denial of access.
It doesn’t matter who you are... it matters what your APN is!
This article will talk about a small trick that a certain virtual OpCoS can resort to in order to deceive its subscribers in the process of providing packet data services. Our focus will be on the process of selecting and using an Access Point Name [APN]. As we remember from the article GPRS from the inside. Part 2, APN is used during the PDP Context activation procedure and is intended to determine the service requested by the subscriber. Services provided by the mobile operator's packet network resources can be:
- Mobile internet
- Intranet VPN access
- MMS
- Wap
- LAN over GPRS
- PTT [Push-To-Talk]
- SMS over GPRS*
* - to provide services for sending short messages, APN is not used and there is no need to activate PDP Context; it is enough to carry out the GPRS Attach procedure.
Let's take a closer look at the mechanisms for selecting and using APN(en) - Access Point Name in a GPRS session. Let's start with the restrictions, APN NOT
:
- end with '.gprs'*
- have special characters in the name (? % # $ *)**
- be less than 1 character and more than 63 characters*
- start with combinations of character sequences: LAC, RAC, SGSN, RNC
- start with operator code (see below)
* - this limitation applies to the so-called
Network ID (see below) ** - only alphanumeric sequences of characters are used: 'A... Z', 'a... z', '0... 9', as well as the symbols '. -' The APN must also start with an alphanumeric character sequence and is not case sensitive on the SGNS side.
Functionally
APN is intended to determine the IP address of the GGSN, which will provide the service requested by the subscriber when activating the PDP context.
Optionally,
the APN consists of two parts - the network identifier (mandatory part) and the operator identifier (optional part):
- the network identifier determines the IP address of the GGSN or several GGSNs and, to a first approximation, determines the type of network to which the GGSN has an outlet;
- operator identifier represents the parameters of the operator network in which the serving GGSN is located and consists of MNC and MCC (for example, mnc009.mcc255.gprs - some operator, Ukraine - which is also called GOI), if this data is not in the APN name, then for subscribers of the operator's home network SGSN will add the so-called Default APN Operator Identifier, specified in SGSN for the subscriber's home network, the so-called. HPLMN*;
* - for a mobile network subscriber, there is the concept of a home network [HPLMN], i.e. network in which the tariffs specified in the contract for the provision of network services will apply, but there is also the concept of a guest or roaming network [VPLMN], in which tariffs will apply according to the roaming agreement between operators. In this case, there will be only one home network for the subscriber, but there may be several guest networks.
The operator ID can be added to the APN in various ways:
- Received from the subscriber upon activation of PDP Context (registered in the APN itself).
- Generated from the subscriber's IMSI if the guest user is roaming and requests access to his home network.
- Obtained from the GOI parameter, which is registered on the SGSN for the network to which the subscriber belongs
The full APN name (including the operator ID) is used to resolve the IP address of the GGSN that will serve the specified APN.
On the side of the local DNS operator, the APN will be “decrypted” from right to left, i.e. the service area of the gprs domain is determined, then the service area of the mcc255 domain, etc. Before activating the PDP Context, the SGSN receives a user profile from the HLR. In the user profile, the APN parameter can indicate the APNs allowed for use by the subscriber, or the “*” icon can be indicated, which allows the use of any of the existing APNs in the operator’s network. If a profile contains a list of several allowed APNs, then the first APN in the list has higher priority than the rest - see examples. For each PLMN, be it Home PLMN or Visitor PLMN, most vendors allow you to register on SGSN, the so-called. Default APN Operator Identifier [DEFAPN], which is automatically substituted as the Network Identifier, i.e. actually replacing the APN requested by the subscriber, but only if the subscriber misspelled the APN or specified an APN that does not exist in the operator’s network. The main idea of using the DEFAPN parameter is aimed at reducing the number of unsuccessful attempts to activate the PDP Context if subscribers made a mistake, i.e. You specified the wrong APN in the connection settings. The use of the DEFAPN parameter is optional and does not affect the overall functionality, i.e. The operator may not purchase licenses to use this functionality. In addition to the DEFAPN settings, usually a mandatory setting on the SGSN is permission to overwrite the requested APN [Override of the requested APN], as well as separate settings for replacing the requested APN for roaming subscribers.
But what prevents the operator from using additional functionality to his advantage... 
The scenarios for the development of events are almost the same for both roaming subscribers and subscribers located in their home network, the only difference is that the parameters for replacing the requested APN must be specified for the PLMN to which the user belongs (i.e., either HPLMN or VPLMN) therefore, all of the following is equally applicable to both scenarios of a subscriber being in a roaming network (VPLMN) and in a home network (HPLMN).
- Smart subscriberGiven:
the subscriber specified in the phone settings an existing APN (for example, opsos.com.ua), to which he is allowed access. His profile on HLR contains a list of APNs allowed to him (for example, in this order - internet, opsos.com.ua, mms.opsos.com.ua).- DEFAPN
Activated,
Override of Requested APN
Permited
The subscriber is in his home network:
to the requested APN SGSN will add the GOI specified for HPLMN (i.e. for our virtual operator it is mnc009.mcc255.gprs), by the full APN name - opsos.com. ua.mnc009.mcc255.gprs will resolve the IP address of the GGSN, which will serve the GPRS session.
PDP Context for the subscriber will be successfully activated according to the APN specified by him (in our case it will be opsos.com.ua), the tariffs for using packet transmission will correspond to the tariffs of the opsos.com.ua access point. The subscriber is in the guest network:
in the guest network, SGSN will add the home network GOI to the specified APN name, based on information from the IMSI, send a request to the DNS server and receive the GGSN IP address in the operator’s home network, then redirect the PDP Context to the subscriber’s home network, i.e. .e. When roaming, subscribers use the roaming SGSN, but all traffic passes through their “home” GGSN. Tariffs for using packet transmission will correspond to the roaming tariffs of the opsos.com.ua access point for the subscriber. - DEFAPN
NOT Activated,
Override of Requested APN
NOT Permited Further developments are almost similar for both roaming subscribers and subscribers in their home network (HPLMN), so we will not consider the two scenarios, but will only point out the main differences. In this scenario, nothing will change, the subscriber will be able to activate PDP Context using the APN - opsos.com.ua, the tariffs for using packet services will correspond to the tariffs of the opsos.com.ua access point. - Typical subscriberGiven:
the subscriber specified an existing APN in the settings, for example - internet (or any other APN existing in the operator’s network), while in the subscriber’s settings on HLR (in his profile) “*” is indicated in the APN parameter.- DEFAPN
Activated,
Override of Requested APN
Permited The subscriber will be able to activate PDP Context using the APN he specified - internet, the tariffs for using packet services will correspond to the tariffs of the internet access point, because The DEFAPN parameter does not participate in any way in activating the subscriber context. - DEFAPN
NOT Activated,
Override of Requested APN
NOT Permited The subscriber will be able to activate PDP Context using the APN he specified - internet, the tariffs for using packet services will correspond to the tariffs of the internet access point. - Almost smart subscriberGiven:
the subscriber specified in the phone settings
NOT
an existing APN (for example, mega.fast.internet), or the subscriber will specify an existing APN in the settings, but which will not be present in the list of allowed APNs in the subscriber profile with HLR. His profile on HLR contains a list of APNs allowed to him (for example, in this order - internet, opsos.com.ua, mms.opsos.com.ua).- DEFAPN
Activated
Override of Requested APN
Permitted In this case, because on the SGSN side, the subscriber profile from the HLR will be received, the first APN in the list will be determined and the PDP Context will be activated using this first APN.There is a small nuance here, because... the subscriber does not have the right to somehow interfere with changing his profile, that is, it is likely that the first APN in the list of APNs allowed for him will be an APN whose usage rates will turn out to be not very low.
DEFAPN
NOT Activated,
Override of Requested APN
NOT Permited In this case, the user will receive a Reject to activate the PDP Context and will not be able to use the requested service until he specifies one of the APNs specified in his profile with HLR. - DEFAPN
- “Gifted” subscriber + a little trick (read LOYALTY) of the operatorGiven:
the subscriber hears the word APN for the first time (or indicated a non-existent APN / made a mistake when entering an existing APN), in his HLR profile “*” is set instead of APN.- DEFAPN
Activated
Override of Requested APN
Permited Let's assume that in the default settings of SGSN for subscribers of the PLMN to which the subscriber belongs, for example, DEFAPN - expensive.net is installed with the “cheapest” (let’s say, packet data transfer under APN expensive.net is the most expensive tariff in the operator’s network) tariffs for using packet transfer data. In this case, because If the subscriber did not specify the “correct” APN, then his requested APN will be replaced with the one specified in DEFAPN, i.e. - expensive.net.Here another “nuance” appears: if a subscriber connects to the network under the specified conditions, then he will pay, i.e. at the expensive.net rate.
DEFAPN
NOT Activated,
Override of Requested APN
NOT Permited In this event scenario, the subscriber will receive a Reject to activate the PDP Context and will not be able to use packet data services. - DEFAPN
Actually, with the help of such small tricks, our virtual cellular operator can deceive its subscribers.
Conclusion:
Always control the settings and parameters that are transmitted in any communication, including when using GPRS/EDGE services in mobile operator networks, because very often messages pop up online about dissatisfaction with data services and high bills for using mobile communications, and sometimes it’s very, very difficult to get some kind of sane answer from the operator.
Z.Y.:
During the writing of this article, not a single cellular subscriber was harmed, because... in our country all operators are “honest” and fluffy 
A little helper:
APN
— Access Point Name
GGSN
— Gateway GPRS Support Node
GOI
— GGSN Operator Identifier
GPRS
— General Packet Radio Service
HLR
— Home Location Register
HPLMN
— Home PLMN
IMSI
— International Mobile Subscriber Identity
LAC
— Location Area Code
MCC
— Mobile Country Code
MNC
— Mobile Network Code
PDN
— Packet Data Networks
PDP
— Packet Data Protocol
PLMN
— Public Land Mobile Network
RAC
— Routing Area Code
RNC
— Radio Network Controller
SGSN
— Serving GPRS Support Node
VPLMN
— Visitor PLMN
Related links (en):
- 3GPP TS 23.003 Numbering, addressing and identification
- PLMN supporting packet based services and PDN
Is it possible without any settings at all?
Thanks to the Access without settings function, you can go online right now, without waiting for you or your phone to understand the sequence of necessary actions. You won't have to pay here.
You can enable the option:
- On request *111*2156#;
- In your Personal Account;
- In the My MTS application
This is a lifeline that will help in emergency situations, not a panacea. So, whenever possible, get your Internet connection in order.
Features of setting up Internet access on a tablet
The method for activating an Internet connection for cell phones can also be used for tablets. If for some reason the necessary configuration parameters were not installed automatically by the provider, the problem is resolved independently.
The easiest way is to order an automated setup of a network access point from your operator via a PC or laptop. But for this, the “Package of three services” option must be activated on the mobile number. To check such information, you need to call the short number 067409.
The provider will send an SMS with a list of all active functions for the SIM card. If there is no Internet in it, an additional request is made to activate it. To do this, use the command 110*181#.
After processing the USSD request, the operator will send a text notification with the auto-configuration parameters. The user will only have to save this data and reboot the device, and the “Settings Wizard” program will do the rest of the work.
What models of WiFi routers does MTS provide?
DIR-615
Our traditional router has proven itself over many years to be a reliable and trouble-free device. This is the router that was previously installed by most MTS subscribers.
Dual-band router Sercomm S1010.MTS
The newest model among MTS routers.
A dual-band router is a router that broadcasts two Wi-Fi networks (that’s why it is also called Dual-Band). This router, like regular routers, distributes the Internet at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. This frequency is now the most common; almost all Wi-Fi routers operate on it. At the same time, it broadcasts a Wi-Fi network at a frequency of 5 GHz. This is what distinguishes a dual-band router from a single-band (regular) router.
How to choose a 4G router
When choosing a device, it is important to consider the following characteristics.
Wi-Fi standards
Modern routers use 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac standards, this will determine the maximum Internet speed on the end device connected to Wi-Fi, the range of operating frequencies (higher frequencies have less interference) and range .
802.11b (legacy) speed 11 Mbps range 2.4 GHz radius up to 50 m.
802.11a (legacy) speed 54 Mbps 5 GHz range up to 30 m radius.
802.11g (new) speed 54 Mbit/s range 2.4 GHz radius up to 50 m.
802.11n new speed up to 480 Mbit/s range 2.4 and 5 GHz radius up to 100 m.
802.11ac (advanced) speed up to 1.3 Gbps 5 GHz range over 100 m radius.
Maximum number of clients
If it is important for you that many devices can be connected to the router at the same time, for example, if you want to use it as a backup access point in the office, then pay attention to this indicator.
Battery capacity and battery life
Do you plan to use your device a lot outside the home and want to stay connected even while fishing? This means that the capacity of the battery is important, that is, how long it works without recharging. Pay attention to models that work as a power bank - for example, from MTS.
Why do you need a 5GHz Wi-Fi network?
Due to the fact that most routers operate at the 2.4 GHz frequency, it is heavily loaded - many devices operating at the same frequency conflict with each other. You've probably paid attention to how many neighboring WiFi networks your apartment can connect to. The more of these networks, the greater the load on the frequency, the slower the Internet works. Using a 5GHz WiFi router allows you to almost completely avoid interference, and as a result, the WiFi connection will be more stable and the connection speed will be higher.
How to use the 5GHz network?
The Sercomm S1010.MTS router simultaneously broadcasts 2 networks – 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The vast majority of devices sold in recent years (and many released earlier) support the 5GHz frequency, so it is better to choose this network when connecting the device for the first time. If you also want to connect an old device, it will not see the 5GHz network, so it will offer you to connect using the 2.4GHz frequency.
Problems of creating a distributed network
and the prospects for its use at objects remote from each other Let's start with the background - it will help to understand why and who may need a slow (in terms of data transfer speed) and relatively expensive (you have to pay for traffic: both incoming and outgoing) organization technology distributed local network using GPRS.
Modern large (and not so large) enterprises with a developed branch network are often in great need of structuring and accounting for their own resources so that they can get a complete operational picture of the work of their own economic model. But on the way to introducing any accounting scheme, most of them are faced with the serious problem of uniting into a single network of branch offices, located not even in regional centers, but in small villages where the Internet is not even planned for the next three to five years. However, the tasks assigned to the staff somehow have to be solved, so usually the employees fill out some paper forms manually, and then once a week (sometimes less often, sometimes more often) they are taken to the regional center, where there is a larger representative office and there is Internet. And only there is data entered and processed (for the second time, mind you!) into some central database of the organization, in which all records are kept.
Of course, first of all, such organizations can be all kinds of city networks, water utilities, oil and gas sales enterprises, that is, large natural monopolies. This means that the most interested in deploying distributed local networks with direct access to each device connected to it are enterprises that want to keep track of any resources: for example, water, electricity, oil, gas at their own facilities, distribution stations, or even end consumers. Therefore, we address this material primarily to IT specialists of such large companies. Let this article become, although not a guide to action, but a description of a possible way to solve this not entirely simple problem.
The organization of such a distributed network was implemented in one of the energy companies. Using her example, we will present information.
It all started with the fact that the management really wanted to establish accounting at all substations, and even do it cheaply - we note that this is a key point, since any entrepreneur wants to get as many opportunities as possible for small and easily predictable expenses. Several options were considered - from the astronomical costs of laying optical fiber throughout the entire region for each substation, to minimalist options such as polling through industrial modems through communication channels over overhead wires (their standard speed is 100 baud). Of course, such polar methods were not chosen: the first - due to the obvious high cost and inconvenience of scaling, the latter - due to the fact that modern equipment refuses to work at speeds below 300 baud (you’ll also have to look hard for this!).
As a result, the IT department of the company in question stopped and to this day is successfully implementing two compromise methods for organizing communications with remote network devices:
- Periodic GSM modem data transmission with payment at different rates from different cellular operators (different operators were chosen due to the fact that, unfortunately, not all cities have built GSM communication base stations yet). You understand that we will not consider this method, it is too specific and not convenient for use anywhere else except for accounting.
- Application of GPRS technologies in GSM communication networks. This is what we will look at in the article.
In fact, the second indicated method can also be implemented in several ways, each with its own specifics:
- A special service ordered from a cellular operator. Traditionally, all operators call it APN. During testing, only MTS and MegaFon were able to provide the service, albeit with reservations.
- Standard GPRS connection of the device to the Internet via a communicator. It does not impose any serious requirements on the operator or the technologies used on the equipment of any of the operators, since it is the most common service.
It must be said that in an energy company the only worthy and self-paying use of a distributed network is commercial metering of electricity supplied to consumers. However, the range of possibilities of a distributed network is somewhat wider, and of course, the approaches to building a network here are completely different, so let’s take a closer look at both ways to create a local network and try to make a few proposals for using the technology in real business.
Attention, it is important to know:
- GPRS technology does not guarantee delivery of every information packet to the recipient! Therefore, when using any of the listed methods, a slight complication of the software is required in terms of controlling data delivery and repeating sending if necessary;
- You should not expect that devices in a distributed network will show good data transfer speeds with each other - one communication channel of a cellular operator dedicated to a GPRS connection implies a speed of 9600 baud! That is, a GPRS communicator of the tenth class (4+2), even with the use of all compression technologies in the data transfer protocol, will show a data reception speed of no more than 38,400 baud and a data upload speed of no more than 19,200 baud. This should be taken into account when developing applications to operate on such a network.
Why not EDGE: in this article we talk about the industrial use of cellular communication technologies, so in its organization we used communicators of special industrial design (that is, certified according to all the rules and necessarily vandal-resistant). Such communicators use only the GPRS standard; for some reason EDGE has not yet found widespread use.
We will indicate the specific brands of communicators that we used in the process of organizing communications: SICON 65 and PGC-1 (the first is based on Siemens, the second is Sony Ericsson). Their limitations: either a standard GSM modem connection or GPRS (no EDGE is provided), and a speed of only 9600 (one channel for reception and one for upload). In fact, the authors, of course, could not miss the opportunity to test at a higher speed (what if the devices have hidden capabilities!?), and tried working at speeds of 19200, 38400 and 57600. In all these modes it was not possible to show the real transfer speed more than 1 kB/s (that is, about 9600 kbaud). You can, of course, try to work with regular cell phones that support EDGE or GPRS class 10-12, but we do not recommend doing this, since in this case the stability of the connection (and its speed!), as well as the performance of household phones , providing it, only the organization’s personnel will be responsible, and not the manufacturer, guaranteeing the quality and speed of the connection on the cellular network resource provided at its disposal.
After all that has been said, I would like to justify the use of such an inconvenient communication service for our purposes as GPRS: at the moment, only networks of cellular operators have a coverage area of about 90% of the most populated areas of the country. Much more advanced WiMAX technology, unfortunately, has not yet become widespread even in large regional centers, not to mention the area of application we are considering (in the territorial sense). That's why we propose adapting GPRS to the needs of companies.
APN, or “Remote access of subscribers to their company’s corporate network”
Here, at first glance, everything is simple: the mobile operator will do everything for the client and everything will work right away, you just need to write an application to open this service on the specified SIM cards and fill out a certain questionnaire.
The first difficulty occurs right here, in the questionnaire. For a person who is not very well versed in network technologies: encryption methods, tunneling and the principle of allocating an IP address to devices - everything listed on one piece of paper in the questionnaire looks incomprehensible. The system administrator will need to get down to business, who will fill out this paper, and at the same time agree on the simplest option for technical and software implementation, convenient for both the cellular operator and the organization.
I would like to warn you in advance that all mobile operators consider this. Tune in for a pause taken by the cellular operator to set up equipment, test channel capacity, and allocate a separate access point for you.
The second problem is that in a regular local network, each computer (or, more broadly, any network device) has its own permanent IP address: either received immediately after installing the OS, if it is on a peer-to-peer network, or received from dhcp- server every time the OS starts (again, usually the same address is assigned each time). In our case, the cellular operator’s software will issue each device that registers on the network again with an address that is not yet occupied in the allocated address range. Keep in mind that cellular networks use software that is somewhat non-standard (for an ordinary administrator), and therefore difficult to configure. It is not a fact that the administrator of the mobile operator in your region will be able to fully configure the service independently. This means that the dhcp server on the side of the access point may not work, that is, it is impossible to guess which device will be assigned which address, and whether it will change if the GPRS connection is accidentally temporarily interrupted! How, then, can you guarantee that the data will be sent to the right recipient?
Of course, this is not a reproach to mobile operators - after all, they are improving the quality of services and the professionalism of their staff by leaps and bounds. However, in the company in question, everything went exactly this way - they allocate only a range of IP addresses and ask us to configure a dhcp server on our side, which, based on a certain unique identifier of a device that has accessed the network, will assign it a once specified, always the same IP -address.
We solved the problems in two ways:
- The system administrator had to set up a tunnel from our organization's dhcp server to the cellular operator's server serving the organization's allocated access point. As it turned out, this problem is completely solvable, although it brings a lot of trouble. Traffic via the Internet for the operation of the dhcp server will be consumed only at the central office, and will be measured in megabytes, and not in network time (which is what we are striving for). However, it is worth keeping in mind that this service is included with all mobile operators only for a subscription fee, with prepaid traffic from 5 to 25 MB included. Consider the economic benefit yourself - if it suits you, then everything is in order. Our organization was not satisfied with this in all cases, so another option was used.
- A more cumbersome solution is to configure network equipment (GPRS communicators) in such a way that each time after registering a device in the GPRS network, it independently, using specially formatted SMS messages (or sending data packets to a static IP address allocated to the Central Server). Internet address) would notify all devices about its new address. Let us honestly warn you that if SMS is not free, then you can spend a lot of money on them - much more than on the useful amount of transmitted information! So a static IP address for the server is the most optimal solution in this case.
APN Pros:
- Working with a separate access point, the use of which minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to your information;
- Addressing in such a network is partially transferred to the cellular operator, and the part that still goes to the IT department staff is not too difficult to solve using quite standard software tools.
- Allows you to achieve permanent IP addressing in a distributed local network.
APN Cons:
- Incomplete implementation of the service - requires the participation of qualified personnel of the organization that needs the APN;
- The subscription fee for each device on the network, at the time of writing, ranges from 5 to 10 USD. per month with prepaid traffic of 10-25 MB;
- High price of traffic (both reception and output are considered) - the prices are the same as for Internet access, while the organization itself is the generator and receiver of information, the Internet is not used - only the communication channels of the cellular operator are loaded;
- A very long period from the moment of sending an application to connect the service to the real opportunity to use it. From a week to two months - depending on the qualifications of the cellular operator’s personnel and the IT department personnel of the interested organization;
- Ties the organization to only one cellular operator, limiting the use of new technologies in those places where base stations of the selected operator have not yet been installed, but stations of another are present.
GPRS Internet connection
In this case, it is assumed that a standard Internet access service is enabled using GPRS technology, as well as the presence of a server with a dedicated static IP address on the same Internet.
The essence of the method is that the device, upon registering in the network of a cellular operator, immediately connects to the Internet and sends an encrypted request to a programmed server address with information about itself and its temporary IP address on the Internet. Next, everything is elementary: two devices with known IP addresses interact on the global Internet on any selected port. The only real weak point of this method is the mandatory requirement for very serious protection of both the transmitted information and the devices themselves, which are constantly on the Internet - they risk becoming a target for hacking at any time.
On the one hand, the method impresses with the simplicity and speed of putting each new device into operation, but on the other hand, it requires quite advanced software (both on the server and on remote computers) that would navigate the constantly changing connections between devices on the network, and it would also be reliably protected from unauthorized hacker attacks from the Internet.
Pros of standard GPRS:
- Quick connection of each new device to the distributed enterprise network;
- No monthly fee in most GPRS tariffs;
- Flexibility in choosing a cellular operator for each specific area: the only important thing is the ability to access the Internet via GPRS;
- Moral satisfaction in the fact that traffic access to your network is paid through a tunnel on the Internet, and not just through the cellular operator’s channels to yourself, as is the case with APN.
Disadvantages of standard GPRS:
- The desired task of obtaining a permanent IP address for each device on the network is not achieved;
- The connection speed is slower than when using APN (there was a dedicated access point, but in the method under consideration, the access point is public, probably working under heavy load);
- What is required is complex software that is “able” to track and organize complex data routing within a distributed network, and can also reliably protect the organization’s important information located on the server and on all devices of this network;
- You will have to pay for traffic, as in the case of APN, for both receiving and transmitting data.
Conclusion
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that organizing a distributed local network for use at objects remote from each other is not an easy task. A solution to the problem can be found, but often it does not quite correspond to the originally conceived plan, and is not always acceptable in terms of its operating cost.
Therefore, we believe that the described methods of organizing communication can be used, rather, as a temporary scheme to wait out the moment when it is not possible to connect the company’s computers into a network using more modern, faster and cheaper methods to operate (ADSL, WiMAX, etc.).
In order to finally determine the range of possible applications of the described technology, we will explain the idea expressed at the beginning of the article about the interest of using a distributed network based on GPRS technologies: for example, at cash desks for accepting utility payments, some standard client-server software is usually used, which allows you to immediately after receiving the payment, distribute how much and where to send funds based on each of the paid receipts. The traffic for each receipt is very modest: a unique personal account of the payer, the amount paid by him, the number of the cash desk where the payment was accepted, and, possibly, some additional official information. That is, if we translate everything into traffic or money, we are talking about tens or hundreds of bytes per receipt, transferred via a GPRS connection from the cashier’s work computer to the central server, which means that even a speed of 9600 baud is enough and paying for traffic will not be too burdensome ( which can be included in the tariff for services). And as a result, we will get a remote workplace equipped with a computer that works on a shared local network (or its imitation), which means that the employer does not need to worry about the daily/weekly organization of the transfer of paid receipts on paper (travel by transport can be noticeably more expensive, than using the cellular communication services we described), and you also don’t have to allocate a special employee (or even several employees) in order to almost manually enter information into the database of the organization’s central server as quickly as possible.
Another interesting use case we see is the so-called telecontrol. In other words, this is an attempt to control remote devices from the operator or dispatcher console. Such devices can be all kinds of switches and regulators. For example, if you need to quickly switch the gas supply from the main line to the backup line, and to do this “manually” you need to go to a gas distribution point, which can easily be located 70 km from the nearest company office. The use of distributed network technology will allow (of course, only for authorized users) to make such a switch without significant time and money spent on moving to the place of regulation.
It seems to us that these are very real examples of saving time and money, as well as increasing the productivity of each individual specialist in the organization. This means that the described methods for creating a distributed network can be in demand and implemented.
APN access point on MTS
Data transfer is one of the main functions of a mobile device. To connect to the Internet, you need to configure the device to work correctly and correctly, namely, create a new APN MTS. What is it for? Let's consider the main purpose and characteristics of this functional unit and analyze the basic methods for setting it up.
What is it and what does it give
Almost every MTS user needs constant and stable access to the network space. But to do this, you will need to perform a number of settings on the device system, namely, activate a new APN. This abbreviation literally translates as access point. The function is a bridge between the consumer's cell phone and the mobile Internet. If it is not implemented or adjusted incorrectly, you will not be able to consume traffic.
APN is a network identifier with which each smartphone is authorized on the World Wide Web. Typically, mobile Internet services are used through various gadgets, tablet computers and modem devices, all of which must be configured to receive and send data packets on the Internet. All the necessary settings are available from the provider on the official website, and the consumer can manually register the necessary characteristics in the phone system or order automatic ones. Using the APN, a cellular operator can monitor traffic consumption from your IP address, install security measures and codes. Correct setup of an access point gives the subscriber:
- The ability to travel across the endless network web.
- Exchange MMS messages with other users.
- Use applications and WAP services.
- Packet radio communication.
Methods for setting up an access point
Now let's move on directly to adjusting the APN on a mobile device. For this, two main methods have been implemented - ordering automatic settings or independent and manual adjustment of the work. Usually, when purchasing a new smartphone or SIM card from a provider, all parameters are already set by default and do not require changes. There are cases when the consumer has to complete a number of procedures in order to receive a package of installations. To submit a request to purchase auto settings, select one of the simple methods:
- Go to the operator’s official website on the Internet. Find the help and support section, then open the corresponding tab with automatic characteristics. In the new window, enter the phone number that needs data transfer. Confirm that you are not a robot by taking a short test.
Click on the send button and wait for the parcel. The package with changes will be sent to the SIM card in the form of SMS. To launch it, just open the notification. After this, be sure to reboot the system. - Call the technical support number – “0890”. It works around the clock. On the line, you will hear the voice of an automatic informant, he will announce the exact state of the balance and offer a number of optimizing options and products from the operator. Then you will be transferred to a direct conversation with a consultant. Dictate your contact number, mobile device model and ask to send settings to it. Wait for the notification. Negotiations with a specialist are not subject to tariffs.
- Visit your nearest MTS promotion and sales center. Contact a free manager and ask him for help in setting up the access point.
It often happens that the required parameters do not reach the consumer. But don’t despair, you can establish connections yourself. Let's consider the procedure for any type of equipment.
On the phone
Changing characteristics on Android looks like this:
- In the main menu of the cellular device, find the settings section.
- After that, select the network connections or mobile data tab.
- Click on the option to create a new access point.
- A window will open in which you need to specify a number of characteristics. Come up with a name for your network - it does not affect the connection. Enter “internet.mts.ru” as the APN email address. Enter your login and security password, they are the same – mts. Set the APN connection type to “Default”.
- All other lines are not required to be filled out.
- Confirm the changes and save them.
The last step is to reboot your mobile phone. A similar list of actions is quite suitable for smartphones with the IOS or Windows Phone operating system. There is only one difference, each manufacturer creates devices at its own discretion, which means that the location of the main menu elements may differ on different models.
Setting up an MTS access point on a tablet
The process of setting up an access point on a tablet computer is no different from the previous method. After all, in fact, such devices are analogues of a smartphone in terms of hardware and functionality. The difference is only in the sizes and ways of displaying information.
How to set APN on the modem
These devices already have all the settings required to log into the network, so the process of completing the task is more than simple. To be able to get on the network, you need to connect the device to a USB port, wait a little while the software and drivers are installed, and then activate the connection. Although, if you have a universal model at your disposal, then, most often, there are no settings in it. In this situation, you will have to write everything yourself.
The procedure will not take much time. Just go into the settings of our software and look for the appropriate section here. We indicate the standard APN indicators, password and, of course, login, as well as a number that looks like this *99#. All that remains is to save the profile and select the default option. Then we calmly take advantage of the opportunities provided.
Attention!
In the case of universal devices, we may encounter previously configured profiles. We need to select our operator's profile and check its functionality. Anything you don't need is simply deleted.
Installing an access point on a modem and router
The company provides its customers with special portable external devices for connecting to the Internet. USB modems of 3G and 4G format are especially popular. They can be purchased at any telecom operator sales office in your locality or ordered online with home delivery. As standard, the kit includes: the device itself, a SIM card, drivers and a brochure with instructions.
Attention! Do not buy equipment from suspicious persons or in unverified places.
To get started, connect the gadget to a USB port on a personal computer or laptop. Next, the terminal should detect the router and run the application installation file. This usually happens automatically. If this does not happen, go to “My Computer” and open the removable media of the same name. Run Autorun.exe manually.
The installation process will not take much time. After a successful procedure, a corresponding icon will appear on the computer desktop. Before starting, reboot the operating system. After that, launch the program, a colorful menu will open. Just press the connect button to start the connection. But if this does not happen, you will need to make the adjustment yourself:
- In the main menu, click on the settings section.
- In the “Network” tab, determine the signal transmission standard. Depending on the model, it can be E, 3G, LTE.
- On the top panel, select to manually scan available signals. A list will open, select the desired item, for example, “MTS RUS 3G”.
- In the right panel, click the Modem Settings button. In the window that opens, enter the connection parameters:
- access point name – “internet.mts.ru”;
- phone number - *99#;
- password and account name – “mts”.
- The process is completed, restart the system.
A situation may arise when the personal computer does not detect the connected device. To resolve this problem, you will need to go to the device manager and find the unidentified device there. Click on it with the mouse and the setup menu will open. Find the device update button. Specify the path to the driver location that is suitable for this modem. Be sure to download it. The required file can also be found on the disk supplied with the equipment.
The operator offers its consumers to use the services of an MTS router for wireless access to the network.
You can take it with you anywhere by charging the battery in advance. It is capable of transmitting a signal to 10 devices simultaneously, but the speed will drop. All settings of the MTS access point of the device are made in a special menu. It looks like this:
- Connect the device to the computer.
- Open any browser and enter “192.168.1.1” in the address bar.
- The system will take you to the internal interface of the equipment. Here you can monitor the network properties and manage the main distribution parameters.
- Open the WLAN section and fill in all the fields there. Write the name of the new network and select the type of encryption on which the protection of your personal data will depend. If necessary, set a security password.
- Save the changes and restart the device.
Changing the password on the MTS Wi-Fi router
Changing this setting will help avoid many unpleasant surprises. The company's specialists strongly recommend using a complex access key for the following purposes:
- limit the use of traffic by third-party devices;
- improve the quality of your home network;
- reduce the load on the signal source;
- keep personal data secret.
The absence of a password opens access to attackers who can:
- steal personal information;
- use the user’s computer to automatically send information prohibited by applicable law;
- use payment card data for personal purposes.
The password can be changed in the modem settings. To log in, you must use the device’s IP address, which is indicated in the address bar of any browser:
- For a D-Link router you need to use 192.168.0.1.
- For TP-Link, Zyxel, Asus modems, enter the address 192.168.1.1.
Once on the login page, you must enter the correct username and password. The main page of the modem web menu should open. Find the Wireless Settings section and go to it. Find the WPA2 Shared Key item and change the key.
Similar actions are necessary in the following cases:
- when suspicious connections appear;
- to prevent uncontrolled use of traffic by children;
- if the owner of the device changes.
Setting a complex password will protect the router owner from unpleasant surprises, including loss of payment card information.
How to disable an access point
The easiest way to do this is to go to Settings on your phone or tablet, select Mobile Data or Mobile Networks, and then turn Mobile Data or Mobile Network to Off.
Important! A similar action can be performed from the notification panel by swiping it down and deactivating the corresponding icon in the quick access curtain.
So, manually setting up an MTS Internet access point, its password, login and name is very simple. All information for popular operating systems is available on the official website.
Restoring the application on the MTS router
Today, router manufacturers have provided software and hardware methods for system recovery. To complete this task, you should adhere to the following scheme of actions:
- Using a suitable browser, enter the number combination 192.168.1.1.
- On the authorization page, enter your username and password.
You can now perform a hardware or software system restore.
The software method consists of performing the following operations:
- Go to device factory settings.
- Find the system web menu section and go.
- Go to configuration.
- Select the reboot item and activate it with the corresponding button.
The hardware method of application recovery is the transition of the device to the parameters prescribed by the manufacturer. You can reset the settings as follows:
- Find the special RESET button located on the back panel of the device.
- Using a long, thin needle, press and hold for 10 seconds.
The router returned to the factory settings specified by the manufacturer in the firmware.
Each user may encounter various problems in the functioning of the Internet signal transmitter. Using simple operations, you can not only configure the mts router, but also return it to the original configuration parameters.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of Wi-Fi equipment from MTS include lightning-fast setup, the ability to interact with the Internet without restrictions (and even unlimited on some tariffs) and throughout the country where mobile communications are available, as well as compact dimensions and very balanced prices, especially for compared to offers from competitors.
Note! There are also some downsides: the connection speed sometimes fluctuates and depends on the time of day, location, and selected settings. It has long been impossible to place an order on the website - you will have to visit the nearest sales office and then choose among the available offers.
The telecommunications operator MTS, in addition to classic network equipment (3G and 4G modems the size of a USB flash drive), also included third-party devices in its digital store - Wi-Fi routers and routers. “New products” come with the “MTS Connect-4” tariff and allow you to use and distribute the Internet in your home region and when traveling around Russia. Setting up the equipment is easy, and connecting is even easier!
FAQ
Question: I made all the settings manually. But I still can’t get online. What to do?
Answer: Check whether the apn and access point name settings fields are filled in correctly. If everything is correct, reboot your cellular device and try again. Check your mobile account balance. It may need to be refilled.
Question: I bought a 4G modem and installed it. Everything works well, but why the speed is so low does not correspond to LTE.
Answer: Most likely, your region does not provide a high-speed mobile data transfer standard. Check with your operator for information. Or the modem settings have a lower default format set.
Question: Will a USB modem work on Windows 8?
Answer: Yes. The router software is fully compatible with all operating systems.
How to connect an MTS router to a computer
There is nothing complicated here. We will need:
- The computer itself, which has a working Ethernet port or at least has a network card.
- A router with free connectors for expanding the network, distributing or transmitting the Internet via a network cable.
- A network cable that you can buy in a store, or perhaps it will already come with the router.
We connect the network cable to one of the additional ports of the router, as well as to the PC itself. Next, we simply look at the connected networks in the computer control panel; the router should be in them.
How to change the password on an MTS router
Everything is just as simple here. All you need is the password and login of the router itself. If they have not been changed before, then they will be the simple word admin.
Next, in the browser, enter 192.168.1.1 as a link; in the page that opens, you need to enter the same login and password. We find the settings, there will be a WLAN item there. Then simply enter a new password, remembering to select “WPA/WPA2-PSK” as protection.
Ready! The password has been changed and can be checked on any device.
How to change the password on an MTS Wi-Fi router for home Internet
The same as changing the router password, because their login and password are the same. Just log in with your details using the link 192.168.1.1 and follow the same steps as in the previous paragraph. The main thing is not to choose simple passwords, because you can gain access to your computer through your home network, and this is not secure.
Conclusion
You can always find out how to set up the Internet on an MTS phone or any other operator on our website. These actions are necessary for the correct operation of the smartphone and uninterrupted access to the World Wide Web.
Sources
- https://ProOperatorov.ru/faq-mts/nastrojki-interneta-mts/
- https://4gconnect.ru/nastrojki-interneta-mts
- https://Vpautinu.com/wifi/tochka-dostupa-mts
- https://mts-is.ru/internet-i-tv/nastrojki/
- https://KakOperator.ru/operators/kak-nastroit-tochku-dostupa-mts
- https://go-MTS.ru/wifi-%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%83%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%8B-%D0%BC%D1%82% D1%81/
- https://mtsdtv.ru/devices/wifi-router/4g/
- https://tvoytarif.ru/mts-manuals/apn-mts
- https://tarifrus.ru/nastrojka-tochki-dostupa-mts/
- https://iguides.comprayexpress.ru/networks/nastroyka-domashnego-interneta-mts/
- https://internetsim.ru/kak-nastroit-router-mts-avtorizatsiya-i-vhod-v-nastroyki/
- https://Vpautinu.com/wifi/mts
- https://tarifam.ru/apn-mts/
- https://KakOperator.ru/operators/instruktsiya-po-nastrojke-domashnego-interneta-mts