Until recently, MTS did not have any offers for subscribers who wanted to connect to a tariff or option with completely unlimited Internet. All Internet options available within the MTS Connect-4 tariff plan require a limited traffic package, after which the speed of Internet access is significantly reduced or completely lost. The maximum that subscribers could count on was night unlimited.
This was the case until recently. Now MTS has truly unlimited Internet! An unlimited amount of traffic is now available to subscribers who have subscribed to the “Smart Unlimited” tariff or the “Internet 4 Mbit/s” Internet option. We reviewed the “Smart Unlimited” tariff in detail in a separate article; in this review we will find out what the “Internet 4 Mbit/s” option is.
A little theory: what is speed, how is it measured?
In order to understand what the speed norm is, it is important to learn to understand its components and special terms. There is a standard by which speed is measured - it lies in understanding what 1 bit, megabit, kilobit are and how they affect the Internet connection. To understand how data transfer speed is calculated, it is important to distinguish the basic terms, but since the bit itself acts as a very small value,
It is customary to immediately group it into groups:
- A kilobit is made up of 1024 bits;
- A megabit is formed from 1024 kilobits.
Previously, the normal speed for wired Internet was considered to be only 128 Kbps, but technologies have changed and now the speed can reach 100+ Mbps.
Mbps - what is it? Conversion of indicators
The file download time can be determined using the formula. For example, to download 100 MB of audio files over a 100 Mbps Internet connection, you need to perform the following calculations to help determine the approximate download time of the audio file:
Convert megabytes to file size (100 MB) to megabits: 100 × 8 = 800 megabits. Divide this amount by the connection speed (100 Mbps): 800 ÷ 100 = 8 seconds.
What should the Internet speed be?
A home connection can be stable, but not high-speed - this depends on the signal quality, incoming speed, location of the coverage area and operator reliability.
You can choose the Internet for your home based on the following classification of norms:
- very slow – up to 512 Kbps;
- slow – up to 2 Mbit/s;
- average – 10 Mbit/s;
- high – 50 Mbit/s;
- very high – from 100 Mbit/s.
Using this feature, you can choose a comfortable tariff for your computer or laptop without experiencing any problems in the future.
What is the Internet
Let's immediately outline some simple and basic concepts. What is the Internet? The Internet is the ability of devices to exchange data with each other.
The device can be a personal computer, tablet, smartphone, etc. Therefore, it is more correct to pose the question - not the speed of the Internet, but the speed of data transfer.
Any data that is transmitted over the network has a digital form and a certain size. Any picture, video file, text - all of this has a size measured in bits.
A bit is the smallest unit of measurement of the amount of information. Previously, when the first computers had very low performance, then the bit was a fairly full-fledged unit of measurement. But in the modern world, technologies already have a much higher speed of information processing, so the bit is no longer used anywhere. Or rather, it is still used, but with the prefixes kilo, mega, giga, etc.
Therefore, now it is much more common to hear the phrase Kilobit (Kbit), Megabit (Mbit ) or Gigabit (Gbit).
To understand, this can be compared to measuring distance. As you know, distance is measured in meters. If the distance has reached 1000 meters, then it is easier to convert it into kilometers and the record will no longer look like 1000m, but 1km.
It is in these units of measurement that providers provide information in their services. For example, the maximum Internet speed via modem for dial-up lines is 56 kbit.
But since we are trying to measure not just the amount of information, but the speed of transmission of such an amount of information, then we need another quantity - time.
Because any speed is measured relative to time - in hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds.
For example, in cars, speed is tied to a clock - km/h (kilometers per hour). That is, at a speed of 50 km/h, a car will cover a distance of 50 km in one hour.
But when measuring the speed of information transfer, it is customary to refer to seconds .
Therefore, the maximum Internet speed via modem for dial-up lines is 56 kbit/s (56 kilobits per second) . That is, in one second you can transfer 56 kilobits of data.
But these types of connections remained almost only in rural areas and small towns.
Otherwise, the connection technologies look like this:
- DSL - an ADSL modem is used as a router, and a telephone line is used as a connection. Internet speed up to 8 Mbit/s.
- Ethernet - router and twisted pair cable, speed up to 100 Mbit/s, less often up to 1000 Mbit/s.
- PON - optical terminal and fiber optic cable, speed up to 1000 Mbit/s.
As you can see, all connections are no longer measured in kilobits, but in megabits.
Therefore, in the modern world, Internet speed is measured mainly in Mbit/s (megabits per second). This is exactly what providers’ advertising banners are full of:
Speed of 100 Mbit/s – is it a lot or a little?
The minimum required speed for comfortable home Internet use is 30-50 Mbit/s. The average user will not receive any benefit from the fact that the contract signed with the provider will set the speed at 100+ Mbit/s. Watching movies, surfing social networks and other entertainment does not require such fast Internet. That is why the question of whether 100 Mbit/s Internet is a lot or a little has a relatively simple answer. This speed is required only by individual subscribers, and is not needed for a regular home network.
How much is 1 mbps?
To begin with, we note that 1 bit is the smallest unit for measuring the amount of information. Along with a bit, people often use a byte, forgetting that these two concepts are completely different. Sometimes they say "byte" when they mean "bit", and vice versa. Therefore, it is worth considering this issue in more detail.
So, 1 bit is the smallest unit of measurement. 8 bits are equal to one byte, 16 bits are equal to two bytes, etc. That is, you just need to remember that a byte is always 8 times larger than a bit.
Given that both units are very small, the prefixes “mega”, “kilo” and “giga” are used in most cases for them. You should know what these prefixes mean from your school course. But if you forgot, it’s worth reminding:
- “Kilo” is a multiplication by 1,000. 1 kilobit is equal to 1,000 bits, 1 kilobyte is equal to 1,024 bytes.
- “Mega” is a multiplication by 1,000,000. 1 megabit is equal to 1,000 kilobits (or 1,000,000 bits), 1 megabyte is equal to 1024 kilobytes.
- “Giga” is a multiplication by 1,000,000,000. 1 gigabit is equal to 1,000 megabits (or 1,000,000,000 bits), 1 gigabyte is equal to 1024 megabytes.
In simple terms, connection speed is the speed of information sent and received by a computer in one unit of time (per second). If the speed of your Internet connection is stated as 1 mbps, what does this mean? In this case, this means that your Internet speed is 1 megabit per second or 1,000 kilobits/second.
Many users believe that mbps is a lot. Actually this is not true. Modern networks are so developed that, given their capabilities, 1 mbps is nothing at all. Let's calculate this speed using the example of downloading files from the Internet.
Keep in mind that mbps is megabits per second. Divide the value of 1 by 8 and get megabytes. Total 1/8=0.125 megabytes/second. If we want to download music from the Internet, then provided that one track “weighs” 3 megabytes (usually tracks weigh that much), we can download it in 24 seconds. It’s easy to calculate: 3 megabytes (the weight of one track) needs to be divided by 0.125 megabytes/second (our speed). The result is 24 seconds.
But this only applies to an ordinary song. What if you want to download a movie that is 1.5 GB in size? Let's count:
- 1500 (megabytes) : 0.125 (megabytes per second) = 12,000 (seconds).
Converting seconds to minutes:
- 12,000: 60 = 200 minutes or 3.33 hours.
Thus, with an Internet speed of 1 mbps, we can download a 1.5 GB movie in 3.33 hours. Here you can judge for yourself whether it will take long or not.
Considering the fact that in large cities Internet providers offer Internet speeds of up to 100 mbps, we would be able to download a movie with the same volume in just 2 minutes, and not in 200. That is, 100 times faster. Based on this, we can come to the conclusion that mbps is a low speed.
First steps to choosing Internet speed for your home
To choose a speed that is suitable for the user, you first need to understand for what purposes the Internet will be used. Depending on your goal, you can choose a provider and enter into an agreement.
Among the main tasks of the Internet are the following:
- to download or watch online videos, listen to music;
- for communication - via video calls, social networks;
- for entertainment in the virtual world of online video games;
- for work – use of news portals, educational sites, to communicate with clients;
- for organizing streaming broadcasts.
The less you perform various tasks on the Internet, the less speed you need, which means the cost of the tariff will decrease.
Internet speed and how it is measured
Surely you know that the speed of movement of a car, person, train or any other vehicle is measured in different units. If we are talking about a car, then its speed can be 100 km per hour, the speed of movement of an ant or a turtle would probably be more logical to measure in meters per hour and the speed of space objects in thousands of kilometers per hour. In the same way, there is a scale for measuring Internet speed.
If the speed of a car is calculated by the number of kilometers the car travels per unit of time, then the speed of the Internet connection is calculated by the amount of information transmitted per unit of time. The unit of information is considered to be a bit or byte. One byte contains 8 bits. And by analogy with many other units of measurement, the prefix kilo (1000), mega (1000000), giga (1000000000), etc. can be attached to these same bits and bytes.
Recently, megabits per second (Mb/s) are most often used to indicate the speed of an Internet connection. For example, a speed of 20 Mbps means that in 1 second you can download (or upload) a file of 20 megabits in size.
Many people often get confused and lost in units of measurement. As we said above, 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. Thus, 20 megabits is 2.5 megabytes (20 : 8 = 2.5). And by analogy, a speed of 20 megabits per second is the same as 2.5 megabytes per second.
It is customary to abbreviate bits with a small letter b and bytes with a capital letter B. This is mainly why confusion arises. 20 Mb/s is 20 megabits per second and 20 MB/s is already 20 megabytes per second. Be careful with this, because the same letter typed in a different case means a value 8 times smaller or larger. So, for example, 20 MB/s is 8 times faster or faster than 20 MB/s.
When talking about Internet connection speed, we usually talk about the maximum possible speed. But not always and not under all circumstances this speed can be achieved.
- Internet speed depends on many factors and may vary depending on the time of day and network load.
- It is important to understand that Internet speed is measured in bits and bytes. Always compare the speed according to the tariff and measured in the same units of measurement.
- The farther the server is located from you to measure the speed of the Internet connection, the lower the speed.
- The more subscribers of the provider are on the Internet at the same time, the slower the Internet connection speed.
For online games
Typically, online games are not too demanding on a high-speed connection; most require a stable signal with a speed of 512 Kbps.
Such connection characteristics will allow you to safely play such popular games as:
- WoW;
- Dota 2;
- World of Tanks;
- GTA.
In cases where the user needs voice chat, the speed should be already 1 Mbit/s. Fans of shooters that require as little ping as possible should look for plans with speeds of at least 10 Mbps.
It is important to understand that downloading and uploading new updates requires a high connection speed, because download files often weigh several tens of gigabytes. The optimal option for such downloads would be a speed of 50-70 Mbit/s is the best option for such downloads.
Terms and meanings
Ping is a tool for measuring signal latency, that is, the amount of time it takes a signal to travel from point A to point B. For example, when you click on a link on a website, it does not open instantly, but with a delay equal to the current Ping . If your connection is working fine, you won't notice the delay as it is measured in milliseconds
— ms. The lower the value, the better.
Vibration - the number of changes in the delay when transmitting a signal from point A to point B, during multiple Ping . Measured in milliseconds
— ms. The lower the value, the better.
Wired connections always have lower latency than wireless connections, which is important when you play online games.
Download - the speed of receiving data from the Internet. The speed at which you download files from the Internet. It is measured in Megabits per second - Mbit /s, less often megabytes per second - MB/s. The higher the value, the better.
Upload – speed of sending data to the Internet. The speed at which you upload files to the Internet. It is measured in Megabits per second - Mbit/s, less often megabytes per second - MB/s. The higher the value, the better.
Megabits and megabytes
The channel speed and download speed are different. Therefore, both megabytes and megabits are not the same thing. ISPs and speed tests measure speed in megabits, while torrent clients measure speed in megabytes.
Sources
- https://SpeedTest24.ru/izmeryaetsya-skorost-interneta/
- https://TechTips.ru/speed/edinitsy-skorosti-interneta/
- https://2ip.ru/article/internetspeed/
- https://FB.ru/article/324716/mbps—chto-eto-za-skorost-korotko-o-bitah-i-baytah
- https://www.syl.ru/article/343565/mbps-chto-eto-znachit-vse-o-skorosti-peredachi-dannyih
- https://vpautine.ru/internet/kakaya-skorost-schitaetsya-normalnoj
- https://SpeedTest24.ru/
- https://speedtest.su/
- https://internet.bizbi.ru/test-skorosti/
[collapse]
For streaming
Normal Internet speed for organizing a stream with video and sound requires a stable, powerful connection. This means that the parameter should not fall below the established norm.
It all depends on the quality of the video that will be broadcast:
- for a video stream in 480p resolution you need only 5 Mbit/s;
- if you want to broadcast an image with 720p quality, you will need 10 Mbit/s;
- For 1080p graphics you need a connection of 20 Mbit/s.
The streamer himself must choose an acceptable speed for his stream, based on the characteristics of his computer, coverage area, and connection quality. Lags and freezes in such broadcasts are a common phenomenon, which can only be eliminated by a powerful (and, most importantly, stable) signal and high speed.
Download speed: Mbit/s and MB/s, how many Megabytes are in Megabit
Good afternoon!
Almost all novice users, having connected to the Internet at a speed of 50-100 Mbps, begin to be violently indignant when they see a download speed that does not exceed several Mbps in some torrent client (how many times have I heard: “The speed is lower declared, here in the advertisement...”, “We were misled...”, “The speed is low, the network is bad...”, etc.).
The thing is that many people confuse different units of measurement: Megabit and Megabyte. In this article I want to dwell on this issue in more detail and give small calculations of how many Megabytes are in a Megabit...
All Internet providers (note: almost all, 99.9%) indicate the speed in Mbit/s when connecting you to the network, for example, 100 Mbit/s. Naturally, when a person connects to the network and starts downloading a file, he hopes to see such speed. But there is one big “BUT” here...
Let's take such a common program as uTorrent : when downloading files in it, the “Download” column shows the speed in MB/s (i.e. MB/s, or as they say Megabyte).
That is, when connecting to the network, you saw the speed in Mbit/s (Megabit), and in all downloader programs you see the speed in MB/s (Megabyte). This is where all the “salt” lies...
Torrent file download speed.
Why is network connection speed measured in bits?
A very interesting question. In my opinion, there are several reasons here, I will try to outline them.
1) Convenient network speed measurement
In general, the unit of information is Bit. A byte is 8 bits, with which you can encode any of the characters.
When you download something (i.e. data transfer occurs), not only the file itself is transferred (not only these encoded characters), but also service information (some of which is smaller than a byte, i.e. it is advisable to measure it in bits ).
That is why it is more logical and expedient to measure network speed in Mbit/s.
2) Marketing move
The larger the number that people are promised, the more people will “fall for” the advertisement and connect to the network. Imagine that if someone starts writing 12 MB/s instead of 100 Mbit/s, they will obviously lose the advertising campaign to another provider.
How to convert Mbit/s to MB/s, how many megabytes are in Megabit
If you don’t go into theoretical calculations (and I think most people are not interested in them), then you can present the translation in the following format:
- 1 byte = 8 bits;
- 1 kByte = 1024 bytes = 1024*8 bits;
- 1 MByte = 1024 kByte = 1024*8 kBit;
- 1 GB = 1024 MB = 1024*8 MB.
Conclusion: that is, if you are promised a speed of 48 Mbps after connecting to the network, divide this figure by 8 - you get 6 MB/s (This is the maximum download speed you can achieve, in theory*).
In practice, add that service information will also be transmitted, the provider’s line will be loaded (you’re not the only one connected to it :)), your PC will be loaded, etc. Thus, if your download speed in the same uTorrent is around 5 MB/s, then this is a good indicator for the promised 48 Mbit/s.
Why is the download speed 1-2 MB/s when I am connected to 100 Mbit/s, because according to calculations it should be 10-12* MB/s
This is a very common question! Almost every second person asks this question, and it is not always easy to answer. I will list the main reasons below:
- Rush hour, line load at the provider : if you sit down at the most popular time (when the maximum number of users on the line) - then it is not surprising that the speed will be lower. Most often, it is in the evening when everyone comes from work/school;
- Server speed (i.e. the PC from which you download the file) : may be lower than yours. Those. if the server has a speed of 50 Mb/s, then you will not be able to download from it faster than 5 MB/s;
- Perhaps other programs on your computer are downloading something else (this is not always clearly visible, for example, your Windows OS may be updating);
- “Weak” equipment (router for example). If the router is “weak”, then it simply cannot provide high speed, and the Internet connection itself may not be stable and often break.
In general, I have an article on my blog dedicated to slow download speeds, I recommend you read it:
Note! I also recommend an article about increasing Internet speed (by fine-tuning Windows):
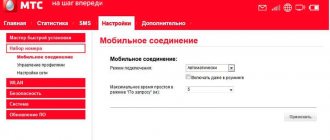
How to find out your Internet connection speed
To begin with, when you connect to the Internet, your taskbar icon becomes active (example icon: ).
If you click on this icon with the left mouse button, a list of connections will pop up. Select the one you need, then right-click on it and go to the “Status” of this connection (screenshot below).
How to check Internet speed using Windows 7 as an example
Next, a window will open with information about your Internet connection. Among all the parameters, pay attention to the “Speed” column. For example, in my screenshot below the connection speed is 72.2 Mbps .
Speed on Windows.
How to check your connection speed
It should be noted that the declared Internet connection speed is not always equal to the real one. These are two different concepts :). To measure your speed, there are dozens of tests on the Internet. I'll list just a couple below...
Note! Before testing the speed, close all applications that work with the network, otherwise the results will not be objective.
Test No. 1
Try downloading some popular file through a torrent client (for example, uTorrent). As a rule, a few minutes after the download starts, you reach the maximum data transfer speed.
Test No. 2
There is such a popular service on the Internet as https://www.speedtest.net/ (in general there are many of them, but this is one of the leaders. I recommend it!).
Link: https://www.speedtest.net/
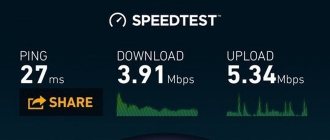
To check your Internet speed, just go to the website and click Begin. In a minute or two you will see your results: ping (Ping), download speed (Download), and upload speed (Upload).
Test results: Internet speed test
The best methods and services for determining Internet speed:
That's all for me, high speed and low ping for everyone. Good luck!
To watch movies and TV series
One of the current tasks of the Internet for user entertainment is showing online videos. Viewing them requires a stable connection so that the file downloads without interruption. To view short videos with low quality (360-480p), only 2 Mbits per second is enough, further increases occur gradually, which means that 5-8 Mbits/s is enough to watch 720p.
Internet requirements increase when viewing files with a resolution of 1080p or in Ultra-HD quality - this requires a connection speed of at least 25-30 Mbit per second.
Units
To measure the speed of a car, kilometers are used as the distance, and hours as the time interval. For example, a car is moving at a speed of 60 km/h.
Bits are used as the minimum unit of measurement for the amount of information, and seconds are used as time.
Since a bit is the smallest unit, nowadays megabits per second (Mbps or Mbps) are used to measure Internet speed. 1024 bits = 1 kilobit (Kbit). 1024 kilobits = 1 megabit (Mbit). A few examples:
All Internet providers use a similar value in their tariff plans - 30, 100, 200 Mbit/s and others. The cost depends on the region of residence and connection technology.
Texts, photographs, music, games, films and TV series are content, a set of files that has a certain weight. For a general understanding, I also took a few examples:
One letter weighs 1 byte, text for ten thousand characters - 176 kilobytes, a song - about 8 megabytes, a movie in Full-HD quality - about 2.3 gigabytes.
Data weight depending on content type
Digital information storage units - table
| Unit | Quantity |
| 1 byte (B) | 8 bits (b) |
| 1 kilobyte (KB) | 1024 bytes (B) |
| 1 megabyte (MB) | 1024 kilobytes (KB) |
| 1 gigabyte (GB) | 1024 MB (MB) |
We constantly receive and send text messages, photos, music in instant messengers and social networks. We download games, movies and TV series using special services.
The speed of downloading and transferring information is measured in the amount of data sent or received per second of time. It directly depends on the speed of the Internet - your tariff plan. The faster the download speed, the faster the data will appear on your device. The required Internet speed depends on your activity.
With a tariff less than 8 Mbit/s, the download speed will be measured in kilobytes per second (KB/s or KB/s). For a tariff greater than 8 Mbit/s - in megabytes per second (MB/s or MB/s). A few examples:
Download movies using a file hosting service at a rate of 60 Mbit/s. The download speed is slightly higher than the tariff due to the cable connection and the large number of uploading clients.
Upload via file hosting service
Download World of Warcraft using the Battle.net client.
For Skype and video calls
Many subscribers use not only the telephone for communication, but also various programs for making video calls. Skype remains the most popular program for this type of communication, but it happens that when making a call the connection is disconnected, the picture becomes pixelated, and the sound sags. In most cases, this problem is related to the quality of the Internet connection.
To communicate safely on Skype, the connection must meet the following criteria:
- voice and video communication requires 100-300 Kbps;
- for a high-definition video call you need at least 5 Mbit/s;
- To create and participate in a general conference, the speed must be from 5 Mbit/s for reception and from 512 Kbit/s for signal transmission.
In fact, it is worth multiplying the described values twice to avoid jumps and deterioration of communication during calls.
What is more important: outgoing or incoming Internet speed?
It is impossible to unambiguously select the most important element, since when comparing two indicators, two important nuances must be taken into account. Firstly, the Internet in the global sense of this phenomenon is unthinkable without outgoing and incoming connections. Removing one of the two mentioned elements will destroy the network. Secondly, every person uses the Internet differently in 2021, so any of the parameters considered may have priority for each user. For those who often talk on Skype, the outgoing connection is more important, for those who like to watch videos, the incoming traffic is more important.
Selecting mobile internet speed
Choosing a tariff for mobile communications often confuses users, because there are many companies and tariff plans on the market that are easy to get confused about. To ensure the highest quality connection, it is better to connect to a well-known operator with a large coverage area, for example, Rostelecom, Beeline or Megafon. The user himself must decide how many megabits per second he will need during the month - many tariffs are connected with 3G or 4G technology, which ensures a high-quality connection.
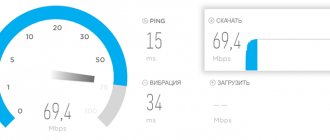
What is an Internet connection speed test?
In 2021, there are quite a large number of different programs and services designed to measure speed quality. They all have an extremely similar operating principle and allow you to obtain accurate results and indicators. At the same time, to carry out measurements, the system sequentially measures every indicator important for a quality connection and allows subscribers to evaluate the current level of communication and compare it with the conditions stated by the provider.
That is, a speed tester is a special program that helps evaluate a connection, and a speed test is the measurement process itself.
It is important to emphasize that the optimal choice would be the service company’s own system on the provider’s official portal.
But, if it’s not there, you should take a closer look at:
- our website;
- internet meter from Yandex;
- portal speedtest.net.
It is worth adding that the programs are equally reliable, regardless of the company that employs the inspector. Therefore, a verification system from, for example, Megafon, is perfect for checking operator services.
What can affect connection speed?
The approximate range of speed fluctuations can be found out by conducting a special test on the Internet, but it is also worth understanding that there are different factors that influence traffic incoming and outgoing from the user.
These factors include:
- frequency of information transmission;
- the presence of malware and viruses on the computer;
- enabled VPN services or proxy server;
- obstacles in the signal path;
- old drivers on the device;
- lack of router and PC settings;
- various interferences;
- distance from coverage area:
- bad weather conditions.
Depending on changes in the listed criteria, the data flow may increase or slow down.
Why does the actual Internet speed differ from that declared by the provider?
When signing a contract for the supply of services with a provider, the user sees the maximum speed that can be achieved. In fact, such figures are unrealistic; the operator is not always responsible for this, because the connection is affected by various interference from other devices. Also, the Wi-Fi router reduces the speed when first receiving and transmitting it to other gadgets. Don’t forget about obstacles in the signal path and the number of simultaneously connected devices. The problem that has arisen can be solved in a simple way - by purchasing a powerful router.