Frequency ranges in Russia are a very confusing topic. But if you dig a little on the Internet, you can find a lot of interesting information on this issue.
- 2 What are frequency ranges
- 3 Which ranges are better - high-frequency or low-frequency
- 4 LTE frequency bands in Russia and in the world
- 5 Which Russian operators provide their subscribers with Internet using LTE technology
5.1 Table: frequency ranges of Russian telecom operators
3G, 4G and LTE - what's the difference
LTE is a standard for wireless high-speed data transmission that replaced the old 3G, which has been actively used around the world since the beginning of the 2000s. Although the data transfer speed has become tens of times higher compared to the third generation standard, LTE technology does not meet the requirements established by the International Telecommunication Union for the 4G standard.
Compare for yourself:
- 3G according to the standard should provide data transfer speeds of 3.5 Mbit/s;
- modern LTE provides download speeds of up to 326.4 Mbit/s and upload speeds of up to 172.8 Mbit/s;
- requirements were put forward for 4G - download speed for devices with low mobility (moving at speeds up to 10 km/h) from 1 Gb/s, with high mobility - from 100 Mb/s.
LTE (Long Term Evolution, literally “long-term evolution”) is a kind of intermediate stage between the third and fourth generations of wireless networks.
Yota tariff for modems
We come to the most interesting part - the tariff plan for modems and routers. After all, many subscribers use Yota 4G high-speed Internet only on computers. However, using a router with Internet distribution, you can access the network from any device. The tariff plan for routers and modems is very flexible - it provides a solid gradation in speed:
- 64 kbit/sec – completely free access, albeit low-speed;
- 512 kbit/sec – Yota 4G internet at this speed will cost you only 400 rubles/month;
- 640 kbit/sec – the subscription fee for this channel will be 450 rubles/month;
- 768 kbit/sec – for access to the network at this speed you need to pay 500 rubles/month;
- 896 kbit/sec – the next gradation of speed for 550 rubles/month;
- 1 Mbit is a quite comfortable speed for surfing, the subscription fee is 600 rubles/month;
- 1.3 Mbit/sec – subscription fee will be 650 rubles/month;
- 1.7 Mbit/sec – network access for 700 rubles/month;
- 2.1 Mbit/sec – subscription fee is 750 rubles/month;
- 3.1 Mbit/sec – good speed for surfing and watching videos for 800 rubles/month;
- 4.1 Mbit/sec – monthly fee is 850 rubles/month;
- 5 Mbit/sec – a solid channel for 900 rubles/month;
- 5.7 Mbit/sec – high-speed access for 950 rubles/month;
- 6.4 Mbit/sec – excellent speed for 1000 rubles/month;
- 7.1 Mbit/sec – fast Internet Yota 4G for 1050 rubles/month;
- 7.8 Mbit/sec – the subscription fee for the channel will be 1100 rubles/month;
- 8.5 Mbit/sec – powerful channel for 1150 rubles/month;
- 9.2 Mbit/sec – quick access to network resources for 1,200 rubles/month;
- 10 Mbit/sec – such a channel will cost 1250 rubles/month;
- 12 Mbit/sec – high speed access to Yota 4G for 1300 rubles/month;
- 15 Mbit/sec – high-speed Internet for 1350 rubles/month;
- The maximum available speed is 1400 rubles/month.
Please note that there are no traffic restrictions here. But the declared speed may differ from the real one for various reasons. At any minute you can set one speed or another - the subscription fee will be recalculated automatically .
In addition, Yota 4G Internet can be connected for 2 hours for 50 rubles or for 24 hours for 150 rubles. Annual tariffs are also provided - 5,400 rubles/year at a speed of 5 Mbit/sec, 6,900 rubles/year for 10 Mbit/sec and 9,000 rubles/year for maximum speed - the discount is quite significant.
Rate this article
0
What are frequency ranges
The entire spectrum of frequencies was divided into bands by the international organization 3GPP. There are only 72 of them, but many of them are inaccessible to the average user and are used for government needs.
Frequency bands (or radio bands) are used not only for mobile Internet access, but also for other purposes:
- TV;
- broadcasting;
- military communications;
- walkie-talkies
They use different bands so that the signals from the devices do not interfere with each other.
In relation to the mobile Internet, frequency ranges may vary depending on the telecom operator and data transmission standard (3G or LTE). In Russia, several sections from 300 to 3,000 MHz have been allocated for these needs. The same radio bands are used for GSM mobile communications.
Theoretically, all of them can be used to transmit data using the fourth generation standard and LTE, but in practice this is not entirely true. The new technology does not immediately replace the old one, and therefore some frequencies are legally assigned to 3G Internet.
Yota tariff for tablets
Tablet computers are not typically used for voice communication or sending messages. Therefore, the Yota tariff for tablets does not include any additional packages - it only contains high-speed unlimited Internet . The tariff plan is activated for a day, a month or a year. More details about tariffs:
- “Day” - a day of access to high-speed Internet Yota 4G will cost 50 rubles. An excellent solution for those who need rare access to the network (for example, only on weekends);
- “Month” - payment for this period is 590 rubles, the possibility of automatic renewal of the package is provided;
- “Year” is the most economical access for 4,500 rubles. Suitable for those who need access to the Yota 4G Internet on an ongoing basis.
If you suddenly want to make a call, a minute of voice communication will cost 3.9 rubles/min. The cost of sending SMS or MMS is 3.9 rubles/piece.
To manage tariffs on smartphones and tablets, a special Yota mobile application is used, available for Android and iOS devices.
Which ranges are better - high-frequency or low-frequency
The lower the frequency, the wider its coverage and better cross-country ability. This gives the user the opportunity to connect to the Internet with a high-quality connection in various remote corners or surrounded by high-rise buildings (and even in the high-rise buildings themselves) in megacities. But such a connection has a lower data transfer rate than high-frequency bands.
For cellular operators, low frequencies (up to 2,000 MHz) are a more profitable solution due to the opportunity to save on equipment. In large cities they are usually used. For the best coverage, the most sophisticated operators combine high and low frequencies. These include, for example, Megafon, MTS, Beeline.
High-frequency bands have higher data transfer speeds, but such towers have a smaller coverage area and wave penetration. They are better suited for open spaces such as suburbs.
Upper and lower frequencies
From a financial point of view, the development of LTE networks at lower frequencies (less than 2000 MHz) is most profitable for operators. Such frequencies penetrate buildings better, but are not able to provide high-speed connections to areas with high population density.
The functions of the upper frequencies are opposite to the functions of the lower ones, so the best option for a high-quality connection is a combination of both frequency channels, which allows you to get rid of “shadow” areas over large spaces.
Also in megacities, there is a tendency to install special devices on the roofs of office buildings to facilitate the spread of high-speed networks indoors.
LTE frequency ranges in Russia and in the world
The frequency bands used may vary from country to country. Because of this, smartphone models produced for use, for example, in the USA or China, will not receive LTE in Russia.
For example, the iPhone SE model A1662, created for the United States, perceives the 20th and 7th bands. But they are still almost undeveloped in Russia. Therefore, when purchasing a smartphone from abroad, you need to carefully check the list of supported radio bands, otherwise you may be left without LTE altogether.
In Russia, five frequency ranges are currently used for fourth generation communications:
- 3 (1800–1880 MHz);
- 7 (2620–2690 MHz);
- 20 (790–820 MHz);
- 31 (450 MHz);
- 38 (2570–2620 MHz).
In the USA, the ranges used are 2, 4, 7, 13, 17, 20 and 25. In Europe - mainly 3, 7 and 20. In Asia - 1, 3, 7 and 40.
Basic LTE modes
The LTE standard is divided into two types: TDD and FDD.
The first implies temporal (from the English Time) division of the signal, and the second - frequency (from the English Frequency). FDD is a more convenient communication mode because, from the point of view of everyday use, it is more stable.
The difference between these concepts lies in the method of loading and unloading data. Thanks to FDD, parallel processing of incoming and outgoing Internet traffic occurs.
Imagine that a user is watching a video on YouTube and at the same time uploading an entire album of photos to the cloud storage. Watching a video will be considered a download operation, and sending a photo will be an upload, and in FDD mode the gadget distributes both operations over different frequency channels.
For example, LTE from the Russian Megafon operates at a frequency of 17 MHz, 11 of which can be used for downloading content, and the remaining 6 for uploading.
Separate traffic processing increases the stability of the speed of each individual process, thereby ensuring a better connection.
TDD processes traffic sequentially. In other words, over the same 17 MHz, both downloading and uploading of data will be carried out - but without separation, but alternately in one channel. The disadvantage of this mode is possible “jumps” in speed.
Currently, Russian cellular operators are striving to combine the operation of TDD and FDD stations. By combining modes into one network, providers increase the overall connection speed.
Which Russian operators provide their subscribers with Internet using LTE technology?
Most major cellular operators have already partially implemented the LTE standard. Among them:
- Yota was the first in Russia to launch an LTE network of 63 base stations. The launch took place in Novosibirsk in 2011;
- Megafon launched LTE the following year, covering Novosibirsk and Moscow. Subsequently, the operator quickly extended the new communication standard to most major cities;
- MTS installed its LTE stations in 83 regions;
- Tele2;
- Beeline;
- Vainakh Telecom (Chechen Republic);
- Tattelecom (Tatarstan);
- "Motive" (KhMAO and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug);
- Win-mobile (Crimea);
- "Volna-mobile" (Crimea).
Table: frequency ranges of Russian telecom operators
| Operator | Frequency (upload/download), MHz | Duplex | Band |
| Yota | 2500–2530 / 2620–2650 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Megafon | 2530–2540 / 2650–2660 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Megafon | 2575–2595 | TDD | Band 38 |
| MTS | 2540–2550 / 2660–2670 | FDD | Band 7 |
| MTS | 2595–2615 | TDD | Band 38 |
| Beeline | 2550–2560 / 2670–2680 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Tele2 | 2560–2570 / 2680–2690 | FDD | Band 7 |
| MTS | 1710–1785 / 1805–1880 | FDD | Band 3 |
| Tele2 | 832–839.5 / 791–798.5 | FDD | Band 20 |
| MTS | 839.5–847 / 798.5–806 | FDD | Band 20 |
| Megafon | 847–854.5 / 806–813.5 | FDD | Band 20 |
| Beeline | 854.5–862 / 813.5–821 | FDD | Band 20 |
LTE frequencies on which Beeline operates
Quite recently, one well-known company introduced a 5G Internet connection to Russian users, which, of course, somewhat smoothed out the “elite taste” of using LTE. However, there are quite a few mobile devices supporting the latest technology, but almost everyone has 4G, and therefore the popularity of the service is not decreasing, but, on the contrary, increasing.
The wireless interface of the described format is incompatible with 2G and 3G, therefore it operates on a separate frequency. LTE includes frequency bands from 1.4 MHz to 20 MHz, the technology supports both frequency division (FDD) and time division division (TDD).
Beeline base stations with LTE support in Moscow and the Moscow region operate in two bands: Band 7 (2600 MHz) and Band 20 (800 MHz). The main advantage of the 800 MHz range is its range, due to which sparsely populated areas require 3 times fewer “towers”. In Moscow itself, this range is also very popular, since, other things being equal, it provides better signal coverage at low frequencies by more than four times.
4G and 4G+ coverage area and a little about the new mobile network network
Every day, 4G and 4G+ mobile networks are expanding into new territories. Thus, on 90% of the capital's area, 4G+ technology from the Beeline provider is publicly available, the connection speed of which is approximately six times higher than the speed of regular 4G.
The coverage of LTE wireless Internet in other regions of Russia is constantly increasing, as evidenced by special coverage maps. You can find out more information about your locality on the company’s official website.
On what basis are frequencies distributed between operators?
In the Russian Federation, only 3–4% of frequency ranges are occupied by civil organizations, which include telecom operators. The rest is distributed between military and public needs.
In Russia, the distribution of radio frequencies is handled by the organization GKRC (State Commission on Radio Frequencies). The telecom operator must apply to use the frequency range of interest. Interestingly, there is no exact data on the frequencies used in the public domain. The applicant will receive information about whether the band is free or not only after reviewing the application (which, by the way, is paid).
The application is being considered by SCRF employees, law enforcement agencies and Roskomnadzor. Each of them may refuse to provide frequencies (the security forces may not even name the reason, citing the secrecy of the data).
If several operators apply for the same resource at once, then the SCRF announces a competition. Points are awarded for using technology and having the right equipment. Whoever scored the most received the right to buy the frequency.
Yota tariff for smartphones
We have already talked about the Yota 4G coverage area and the subscriber devices used. Now we need to talk about tariffs. First, let's look at the tariff for smartphones. There is only one, but it is flexible and customizable:
- 200 minutes of calls within Russia and 2 GB of traffic – the subscription fee is 370 rubles/month;
- 500 minutes of calls within Russia and 6 GB of traffic – the monthly fee is 450 rubles/month;
- 800 minutes and 12 GB of traffic – subscription fee is 780 rubles/month;
- 2000 minutes and 15 GB of traffic – the subscription fee will be 1250 rubles/month;
- 5000 minutes and 30 GB of traffic – costs 2850 rubles/month.
Many other combinations are available.
For another 50 rubles/month you can connect to unlimited SMS, and for 15-60 rubles/month you can connect to unlimited applications that allow you to get unlimited access to social networks and instant messengers. In domestic Russian roaming, the cost of services does not change . But if you spend more than 30 days in another region, the subscription fee will change in accordance with special roaming rates - they are 20-30 percent more expensive).
If the package of minutes is exhausted, you can connect an additional package - 100 minutes of communication will cost you 180 rubles. If the package is not needed, then the cost per minute will be 2.5 rubles. As for SMS and MMS, they will cost 2.5 rubles/piece.
How to find out the 3G, 4G frequency on your smartphone
To find out the frequency or range in which your mobile Internet operates:
- Disconnect from Wi-Fi and turn on mobile data (Cellular).
- An icon at the top of the screen next to your carrier's name will indicate whether you're connected to 3G, LTE, or 4G.
- Open dialer and enter the code. For Android - *#0011#, *#*#4636#*#* or *#*#197328640#*#*, depending on the version. For iPhone - *3001#12345#*.
- The menu that opens varies greatly among different smartphone models. You need to find in the menu Freq Band or Frequency (if you are connected to 4G) or WCDMA (if you are on a 3G connection). This field will indicate which frequency you are connected to.
In this menu you can see the status of the wireless network
Having understood the pros and cons of different frequencies, you can choose the operator whose coverage will suit you best. This way you can improve the quality and speed of your mobile Internet.
All about 4G/4G+
Unlimited 4G Beeline requires replacing the SIM card and checking your smartphone to see if it can support the network. It can initiate the transmission of signaling data packets of 1 KB per hour. This indicator is independent of installation configurations. If Beeline 4G does not work, you will have to configure it. To find out if your mobile device is suitable for receiving a signal in this mode, the following options are available:
- command *705#;
- Personal Area;
- assistance from an office or call center operator.
The combination *705# will also inform the subscriber about the presence of an active connection. Phones and computer equipment based on iOS, Android, and Windows Phone are capable of functioning through 4G. Supporting Models:
- Galaxy Alpha (SM-G850F).
- Note Edge (SM-N915F).
- Galaxy S6 (SM-G920F) – B7, B20.
- Galaxy S6 Edge (SM-G925F) – B7, B20.
- Honor 6 (H60-L04).
- Ascend Mate 7 (MT7-L09).
It is important to study the Beeline coverage area where the network connection will operate so that the Beeline 4G Internet speed is maintained in the correct mode.
The territory is constantly expanding. More than 90% of the coverage has been developed in Moscow. As you leave the area, the signal will become weak and stop working in some areas.
LTE frequencies on which Beeline operates
To switch to 4G, you need to adapt the device and the required frequency. LTE Beeline is a standard variation of wireless high-speed data transmission that has been modernized. Now the network frequency is 1800 MHz and 800 MHz, which allows you to surf the Internet at high speeds.
Connection
To connect to mobile 4G Internet, a request is provided to the number 06740909871. After entering the command and pressing the call key, the autoinformer will inform you in a response SMS message that the connection was successful. If an “error” or “failure” occurs, additional settings will be required. Installation files can be ordered via the USSD combination *110*181#. When the configuration arrives, it is activated by dialing 0880.
We recommend: Honest reviews of the Beeline Smart box turbo router
Use through your personal account
After checking the device and purchasing a new SIM card, you will need to enable network service in the new mode. To connect 4G to a Beeline number, additional options are provided: personal visit to the office, remote mode. For self-activation, it is better to use your profile on the operator’s virtual portal. Instructions:
- Register on the portal, follow the link.
- Scroll down the page and click the button that says “Start using 4G/4G+”, it will appear only after registration.
- After activating the option, the subscriber can change the tariff and connect additional services to optimize use.
It is important to study the area where 4G is available, otherwise the connection will work poorly or periodically disappear. For this purpose, there is a “Coverage Map” section on the same page.
Iota network signal level
Iota has high-quality Internet coverage. But as users grow, the quality of the Internet connection can noticeably deteriorate. To check the signal level, you need to open any browser installed on a desktop computer or laptop and enter the combination of numbers in the address bar - 10.0.0.1.
You must first connect the device to the PC and place it in a place with good signal reception.
To determine whether the signal level is good, you need to consider an example of connecting a Yota Many (lte) router.
To determine the signal level, you only need two parameters shown in the picture - RSRP and SINR. The first indicates the signal strength from the Iota base station. The smaller this parameter, the more powerful the signal level. SINR is a parameter indicating the signal to noise ratio. If this parameter is 0 dB, then the signal is equal to the noise level. This is the key to a better Internet connection.
It follows: the larger the RSRP and SINR parameters, the better the network signal level.
It is also worth mentioning the existence of a special map that displays the network signal strength. The user must find his location on the map. If this area on the map is shaded, then the Internet signal should be simply impeccable, but if the color is light, then the signal may periodically disappear and the connection will be unstable.
What should residents of regions with poor coverage do?
Yota Internet coverage is in great demand throughout Russia, but there are regions where the quality of communication leaves much to be desired. There are also cases when the signal is satisfactory and suddenly disappears.
First of all, you need to consider the main reasons why problems with the Internet may arise.
- The provider has changed the directions of the radiation sectors. This is the case when the user is in the network coverage area, perhaps even close to the base station, but the signal is unstable and weak. The direction of radiation sectors is periodically changed by all mobile operators; this is necessary for dynamic load distribution in different coverage areas.
- New obstacles appeared in the signal path (plantings, building structures, etc.). This problem is not common, but it does occur.
- Operator Yota has closed the service. Such situations arise when operators need to reorganize the network. This entails moving base stations.
Another fairly common reason is a large number of users connected to one base station. In this case, it is recommended to replace the insufficiently powerful base station. If company employees do nothing, the signal for each user deteriorates and the speed drops.
There are also several proven ways to increase the level of the received signal and improve the quality of the Internet connection.
- Place the Yota 4G modem as close to the window as possible. The most suitable place is directly on the windowsill. To connect the modem to an Internet center like Keenetic, use a special extension cord with a suction cup for mounting on a hill. Experts strongly recommend purchasing a high-quality shielded USB extension cable.
- Alternatively, you can try connecting the USB modem through a hub with its own power supply. This approach is especially relevant if the quality of the 4G/LTE received signal is poor.
- Place the modem away from potential interference - sources of high-frequency waves. This will reduce noise and improve the quality of the useful signal.
Note! The performance of a 4G/LTE modem is negatively affected by nearby modems, routers, smartphones, tablets, PCs, etc. For example, even an external hard drive equipped with a USB 3.0 port can reduce the speed
Some routers are additionally equipped with a duplicate Mini/Micro USB socket, and not just a standard plug/connector. Thanks to this design solution, the pocket router can be connected to the Internet center via a network cable.
To strengthen the signal, you can additionally purchase removable antennas of different powers. First you need to familiarize yourself with the possibility of installing it on a specific router model.
Mobile operator Yota is rapidly developing and gaining momentum. However, before using the services of an operator, you need to make sure that there is excellent coverage in the region.
Further development of LTE
Despite the launch of testing of fifth generation networks in the world, some regions of the Russian Federation still do not even support 3G. In connection with this circumstance, it is worth predicting, first of all, the widespread development of LTE technology. Also, fourth-generation networks represent a non-alternative way of accessing the Global Wide Web in a number of Russian regions, which encourages domestic cellular operators to develop the 4G standard.
In some cases, a wired connection is simply impossible, which contributes to the spread of wireless technologies: the capabilities of cellular stations can be expanded thanks to special signal repeater antennas. The user can independently purchase such an antenna. It is important to consider that each repeater only works with certain frequencies and mode (FDD or TDD).
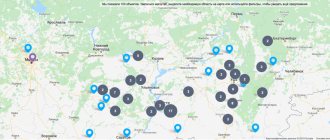
Coverage map Yota, MTS. MegaFon and Tele2 in the Russian Federation
Below you can see an interactive map of network coverage areas.
To see which operator has the best signal in your city or region, select it in the top panel of the map.
If the map is not displayed, and instead you see an empty window, there may be several reasons for this:
- The page has not yet loaded 100%. Wait a while or just try updating it.
- The map scale is too large or, conversely, too small. Try zooming in on the map using the mouse wheel.
- Your locality does not have an operator network.
- If you are from Ukraine, then your Yandex.Maps resource is blocked
Loading a coverage map of Yota, MTS, Megafon, Tele2 operators
Color indicators found on the map:
Iota: 4G network, 3G network, possible 4G coverage, 2G connection
MTS: 4G Internet, 3G Internet
Megafon: 4G network, 3G network
Tele2: 3G internet, 4G internet
Based on the data presented on the map, we can conclude that the best signal is received by residents of large cities of the Russian Federation, such as Moscow, St. Petersburg, Khabarovsk, Ufa, Kazan and many others. The rest have a weaker signal, but this does not mean that the operator has given up on high-speed Internet. As before, the Yota team continues to install their towers, increasing coverage every year!
But there are also several features that are worth considering:
- First. The map did not take into account the relief and general specifics of the area. It was made on the principle of direct visibility of which path the signal will travel from a cell tower to a specific locality.
- Second. Even where excellent 4G network reception speeds are noted, they may change from time to time. This is due to the fact that the tower is overloaded with the number of requests or the signal is simply hampered by urban development, and in particular by its density.
- Third. The distance from the tower also greatly affects the network connection and communication in general. Even when it is located in direct line of sight, problems with the Internet can sometimes arise due to the banal distance.
The best option for checking network speed and reception is to do it yourself, regardless of the data seen on the interactive map. The operator is happy to offer this opportunity in the form of a test drive for a period of 7 days when you purchase a Yota modem. If, while using it, you observe an extremely sad situation with the signal strength and other indicators, then you can return everything to the nearest Yota office, get your money back and find an alternative option.