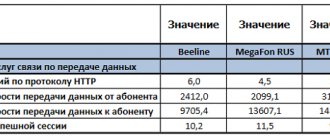
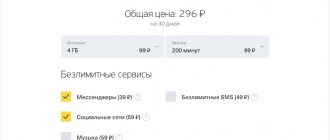
In total, the evolution of mobile communications took place in the following order - 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G. At the time of writing and publishing this article, the generation of new 5G mobile communications is already being tested in some countries and cities:
- USA in cities: Houston, Indianapolis, Los Angeles and Sacramento
- South Korea in various major cities, as well as in Seoul.
- Switzerland – 54 cities.
- Great Britain.
- Italy.
- Spain.
- Germany in several cities: Bonn and Berlin.
- China – 50 cities.
Also, preparations are already underway for the introduction of the sixth generation of mobile communications - 6G in the second half of the 2020s - 2030s.
Cellular generations
- this is a set of functionalities for network operation within the framework of certain standards, including: subscriber registration, information transfer, encryption, roaming, as well as a set of various services provided to the subscriber. And each generation includes different standards, which are improved with each generation. So which communication standard is better? Let's figure it out now!
These cellular communication standards are divided into 2 types:
- Analogue – 1G
- Digital – All other mobile communication standards (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G).
| Cellular generations: | 1G | 2G | 2.5G | 3G | 3.5G | 4G | 5G (new generation cellular communications) |
| Cellular standards: | AMPS, TACS, NMT | TDMA, CDMA, GSM, PDC | GPRS, EDGE (2.75G), 1xRTT | WCDMA, CDMA2000, UMTS | HSDPA, HSUPA, HSPA, HSPA+ | LTE-Advanced, WiMax Release 2 (IEEE 802.16m), WirelessMAN-Advanced | |
| Advantages: | Analog standard | Digital standard, SMS support | Packet data transfer, speed increase | Increasing capacity and speed up to 2 Mbit/s | Speed increase | Increased capacity, IP-oriented network, multimedia support, increased speed up to hundreds of Mbit/s | Speed from 1 Gbit/s, average number of simultaneous users - 1 million per km², latency up to 1 ms, increased energy efficiency |
| Data transfer rate: | 1.9 kbps | 9.6 - 14.4 kbit/s | 115 kbit/s (1 phase), 384 kbit/s (2 phase) | up to 3.6 Mbit/s | up to 42 Mbit/s | 100 Mbit/s - 1 Gbit/s | from 1 Gb/s, 6.5 Gb/s |
| Operating frequency (MHz): | 900,1800. | 900,1800,2100. | 800,1800,2600. | ||||
Cellular communication is...
Cellular refers to Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), which divides a geographic region into sections called cells. The purpose of this division is to make maximum use of the limited number of transmission frequencies.
Cellular communication is a form of communication technology that enables the use of mobile phones.
A mobile phone is a two-way radio that allows simultaneous transmission and reception.
Cellular mobile communications are based on geographical division of communication coverage area. Each cell is allocated a certain number of frequencies (or channels), which allow a large number of subscribers to simultaneously carry out conversations.
A common element of all generations of mobile communication technologies is the use of certain radio frequencies (RF), as well as the reuse of frequencies. This makes it possible to provide services to a large number of subscribers while simultaneously reducing the number of channels (bandwidth). It also allows for the creation of wide networks, fully integrating the advanced capabilities of the mobile phone.
Increased demand and consumption, as well as the development of various types of services, have accelerated the rapid technological development of modern networks, as well as the continuous improvement of cellular devices themselves.
Virtual operators of the MTS network
MTS mobile networks are among the oldest in the post-Soviet space. They were formed on the basis of open frequencies for military and civil air navigation in 1993. By 2021, MTS is one of the industry leaders, providing communication services to more than 105 million subscribers.
MGTS
PJSC Moscow City Telephone Network (MGTS) began operating as an MVNO in 2014 after receiving a license (2013).
The service package combines digital TV, mobile communications, broadband Internet access, and fixed telephony. The company also provides video surveillance and security alarm services and other household services.
MGTS subscribers have the opportunity to analyze the parameters and quality of communication online, as well as remotely monitor the volume of services provided.
How mobile communication works
Each mobile phone uses a separate temporary radio channel to communicate with the cell site. This site supports communication with many phones simultaneously, using one channel per phone. The channels use a couple of cellular frequencies:
- Direct line for transmission from a cell site.
- A reverse line so that the cell site can receive calls from users.
Radio energy dissipates over distance, so cell phones must remain close to the base station to maintain communication. The basic structure of mobile networks includes telephone systems and radio communication services.
Where is mobile communications going?
In developed regions, the main direction of development of mobile communications for the near future is convergence: providing subscriber terminals with automatic switching from one network to another in order to most effectively use the capabilities of all communication systems. Automatic switching, for example, from GSM to DECT (and vice versa), from satellite to terrestrial communications, and when providing wireless data transmission, will allow automatic switching, for example, between GPRS, EDGE, Wi-Fi and other standards, many of which (for example, WiMAX) are just waiting in the wings.
How cellular communications work (for dummies)
The process begins by activating the chip by entering the PIN code of the inserted SIM card. Then the cellular signal is transmitted via control channels. The response from the called number is transmitted over a free control channel to the base station antenna, from where it is transmitted to the mobile switching center.
The switching center searches for the base station with the maximum signal strength of the cellular subscriber's cell phone and switches the conversation to it.
Early telephone system architecture
Traditional mobile service was structured similarly to television radio broadcasting: one very powerful transmitter, located at the highest point in an area, would broadcast over a radius of up to fifty kilometers.
The cellular concept structured the telephone network differently. Instead of using a single high-power transmitter, many low-power transmitters were placed throughout the cellular coverage area.
For example, by dividing an area into one hundred different areas (cells) with low-power transmitters using twelve conversations (channels), the system capacity could theoretically be increased from twelve conversations or voice channels using one high-power transmitter to twelve hundred conversations (channels). ), using hundreds of low-power transmitters.
The urban area is configured as a traditional mobile phone network with a single high-power transmitter.
Mobile communication system using cellular concept
Interference problems caused by mobile devices using the same channel in adjacent areas have proven that all channels cannot be reused in every cell. Although this affected the effectiveness of the original concept, frequency reuse has become a viable solution to the problems of mobile telephony systems.
Engineers discovered that the impact of interference was not related to the distance between zones, but to the ratio of the distance to the power (radius) of the zones' transmitters. By reducing the zone radius by fifty percent, service providers can quadruple the number of potential customers in the zone.
Systems based on areas with a radius of one kilometer will have one hundred times more channels than systems with areas within a radius of ten kilometers. Speculation led to the conclusion that by reducing the zone radius to a few hundred meters, millions of calls could be handled.
The cellular concept uses variable low power levels, allowing cells to be selected according to subscriber density and the needs of a given area. As the population grows, cells can be added to accommodate this growth.
Cellular frequencies used in one cluster of cells can be reused in other cells. Conversations can be transferred from cell to cell to maintain constant telephone communication as the user moves between them.
Cellular radio equipment (base station) can communicate with mobile phones as long as they are within range. Radio energy dissipates over distance, so mobile phones must be within the operating range of the base station. Like the early mobile radio system, the base station communicates with mobile phones through a link.
A channel consists of two frequencies: one for transmitting to the base station and one for receiving information from the base station.
Which mobile communication standard is better?
At the moment, the fastest communication is provided in 4G networks. The fourth generation of communication already has fairly good coverage in Russian cities, and also has a very good data transfer speed of 100 Mbit/s - 1 Gbit/s, which makes its use very desirable for many Russians users and clients. But you shouldn’t forget that power consumption in 4G is usually slightly higher than in the previous generation (3G). According to some data, energy consumption in fourth generation networks is 20% more than in 3G. And here the conclusion is very appropriate. Each user, if possible, already chooses 4G or 3G to use. To have more speed and energy consumption or vice versa, it depends on the person and the case
Cellular System Architecture
Increased demand and poor quality of existing services have prompted mobile service providers to explore ways to improve service quality and support more users on their systems. Since the amount of frequency spectrum available for mobile cellular use was limited, efficient use of the required frequencies was necessary for communications coverage.
In modern cellular telephony, rural and urban areas are divided into districts according to specific service rules. Deployment parameters, such as number of divisions and cell sizes, are determined by engineers experienced in cellular system architecture.
Provision for each region is planned according to an engineering plan that includes cells, clusters, frequency reuse and handover.
A cell is the basic geographic unit of a cellular system. These are base stations that transmit signals across small geographic areas, which are represented as hexagons. The size of each varies depending on the landscape. Due to limitations imposed by natural terrain and man-made structures, the true shape of the cells is not a perfect hexagon.
A cluster is a group of cells. No channel is reused across the cluster.
Since only a small number of radio frequencies were available for mobile systems, engineers had to find a way to reuse radio channels to carry more than one conversation at a time. The industry's solution was called frequency scheduling or frequency reuse. Frequency reuse was realized by restructuring the mobile phone system architecture into a cellular concept.
Cellular standards are as follows: The concept of frequency reuse is based on assigning each cell a group of radio channels used within a small geographic area. Cells are assigned a channel group that is completely different from neighboring similar units. Their coverage area is called a fingerprint. This fingerprint is bounded by a boundary so that the same group of channels can be used in different cells that are far enough apart that their frequencies do not interfere.
Cells with the same number have the same set of frequencies. If the number of available frequencies is 7, the frequency reuse ratio is 1/7. That is, each cell uses 1/7 of the available cellular channels.
Operating principle
Cellular networks exploit the ideas of media access control (MAC). Complete analogue of the wired version. Data is multiplexed, saving resources. The physical environment determines the specific protocol design. The radio signal changes due to optical effects, weather conditions, time of day, and year. The reception quality is constantly fluctuating. The obvious solution is to increase the power, but this measure also increases the interference phenomenon. The number of errors is growing. Approximate ratios:
- Wired network – the number of errors is less than a millionth.
- Cellular communications - the number of incorrect packets is over a thousandth.
The difference exceeds three orders of magnitude. Terminals have to use half-duplex mode. The energy of the transmitted packet is much higher than the received signal. Features of the circuitry allow interference. The leakage of so much power into the reception path of a full-duplex device interferes with the decryption of packets.
Controlled Access Scheme
An operations controller is appointed to coordinate the distribution of resources. More often the role is played by a tower, an access point. The terminal executes a pre-programmed program for allocating channels, frequencies, time slots, and antennas. No conflicts are guaranteed.
Cellular system
- TDMA. Time division.
- FDMA. Division by frequency.
- OFDMA. Orthogonal frequency access.
- SDMA. Spatial division.
- Poll.
- Token Ring.
Dynamic resource allocation brings undeniable benefits to heavily loaded networks. Because free access protocols spend the lion's share of time preventing collisions. The terminal checks the activity of subscribers one by one, using random number algorithms, providing slots for those wishing to transmit information.
A common disadvantage of controlled access schemes is the difficulty of covering extended areas with cells. Service information packets take up a lot of space.
Frequency division
Evolutionarily oldest cellular technology. Within a session, a request receives a unique frequency. An empty channel is marked with an appropriate identifier, allowing further distribution of the resource.
The method is used in narrowband systems, where the length of a symbol significantly exceeds the average message delivery time. Variable bitrate requires modification of the method, allocating a band according to the width of the signal spectrum. But frequency division will allow you to organize a duplex channel.
Time division
The controller allocates a fixed time interval to the subscriber. Without taking into account the slot load.
Multiplexing by signal spectrum width
The circuit combines time division and frequency division. There are 2 daughter species:
- Pseudo-random restructuring. Current frequency and time channels are composed of a strip of narrow segments. A subscriber broadcasting a narrowband signal receives a slot. The entire time is allocated, the frequency is allocated free (can change) at the current moment. The frequency change can occur several times during the duration of one bit of information.
- Direct sequence method. The bit is encoded by a pseudo noise signal (PNS) modulating the carrier. The spectrum is greatly expanded, allowing for a lower signal-to-noise ratio. This eliminates mutual interference between terminals and reduces power density. The use of PSN allows several subscribers to operate a single frequency.
Orthogonal frequency division
The electronic filling of the receiver performs the inverse Fourier transform of the signal. The spectrum arrives in parts, transmitted by spaced carriers. The parallel use of several narrow channels provides a chance to improve resource utilization.
Free access protocol
The terminal provides resources randomly. Lack of coordination implies the occurrence of collisions. Ideal choice for low-load networks. Otherwise, system performance drops sharply. But the hardware implementation is extremely simple.
- ALOHA.
- CSMA.
- CSMA/CA.
Obstacles in the development of cellular communications
Unfortunately, economic considerations have made the concept of creating complete systems with many small areas impractical. To overcome this difficulty, system operators developed the idea of cell splitting. When a service area becomes crowded with users, this approach is used to divide one zone into smaller ones. In this way, urban centers can be broken down into as many areas as needed to provide an acceptable level of service in high-traffic areas, while larger, less expensive cells can be used to cover outlying rural areas.
The latest obstacle in the development of the cellular network stems from a problem that arose when a cellular subscriber moved from one cell to another during a call. Since adjacent areas do not share the same radio channels, a call must either be dropped or transferred from one radio channel to another when a user crosses the line between adjacent cells.
Because call drop is not acceptable, a handover process was created. Handover occurs when the mobile telephone network automatically transfers the call to another radio channel when the mobile device crosses neighboring cells.
During a conversation, the two parties are on the same voice channel. When a mobile device leaves the coverage area of a given cell site, reception becomes poor. At this point, the cell site being used requests handover. The system switches the call to a higher frequency channel at the new site without interrupting the call or alerting the user. The call continues as long as the user is talking and the caller does not notice the handoff.
Combined virtual operators
This category includes such virtual operators that rent capacity and equipment from several large companies providing communication services.
MATRIX mobile
MATRIX Telecom LLC is one of the first virtual operators in Russia, founded in 2003. At the moment, the radiotelephone operator operates on the platforms of the MegaFon, VimpelCom (Beeline brand) and Tele2 networks. Coverage map - Moscow and Moscow region.
The operator offers a range of services aimed at private clients and legal entities. There is a varied range of tariffs designed for calls within Russia and around the world.
Aiva-Mobile
The company began its activities as an MVNO in 2014 on the platform of the Tele2 networks in Moscow and St. Petersburg. The range of tariffs is focused on calls within Russia and the CIS.
Aiva-Mobile offers its customers a card with two numbers linked, which is not only convenient for long-distance communication, but also much cheaper than other operators. The company is working to expand its coverage map, and also enters into contracts with other countries for cooperation in order to create low-cost roaming.
A full-fledged cellular operator infrastructure has been created for Aiva Mobile, including a billing system, its own GMSC switch, HLR system, data channels and other technical components.
Gazpromtelecom
Gaztelecom is a combined operator created in 2013. Works on network platforms of leading Russian operators. It has a fairly wide coverage map. Gazprom is seeking to transfer all employees to MVNO Gaztelecom, and their number is about half a million. Offers its subscribers a smooth transition by maintaining their phone number or purchasing a new one. The range of tariffs is varied, starting from 100 rubles. up to 2000 rub.
Cellular System Components
The cellular system offers mobile and portable telephone exchanges the same service as fixed-line exchanges over conventional wire loops. It is capable of serving tens of thousands of subscribers in a large metropolis. A cellular communications system consists of the following four main components that work together to provide mobile communications services to subscribers:
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
- Mobile telephone exchange (MTSO).
- Cell site with antenna system.
- Mobile subscriber unit (MSU).
The PSTN consists of local area networks, exchange area networks, and long-distance networks that connect telephones and other communications devices around the world.
MTSO is the central office of mobile communications. It houses the communications switching center (MSC), field control and relay stations for switching calls from cell sites to wireline central offices (PSTN).
The term "cell site" is used to refer to the physical location of radio equipment that provides coverage in a cell. The list of hardware located at a cell site includes power supplies, interface equipment, radio frequency transmitters and receivers, and antenna systems.
The mobile subscriber unit consists of a control unit and a transceiver that transmits and receives radio transmissions to and from the cell site. Three types of MSU are available:
- Mobile phone (typical transmission power 4.0 W).
- Portable (typical transmit power 0.6 W).
- Transportable (typical transmission power is 1.6 W).
Virtual operators on Megafon networks
One of the Big Three operators, operating in the telecommunications services market since 1993. It has the most modern and powerful equipment in Russia and a stable coating. All this provided opportunities for the development of virtual networks based on Megafon.
Yota
The corporation was formed in 2007. In 2014 began its active work selling cards based on Megafon. The cost of tariff offers varies within standard prices across the country. The quality of the services provided is quite high, with an extensive coverage map. The main feature of the operator is unlimited communication between Yota subscribers. The average monthly cost is 550 rubles. In September, the company launched a new project for tablet gadgets, allowing unlimited use of some applications.
Gars Telecom
This MVNO has existed for subscribers since 2003. Currently it operates on Megafon network equipment. It provides its services to clients in Moscow and St. Petersburg. The development trend is in the B2B segment. This is the area of office, hotel, and industrial real estate. Gars Telecom provides full cycle telecom services: fixed and mobile communications, Internet access, creation and rental of channels and infrastructures and many others. Network subscribers note the speed of work of managers in connecting, budget tariffs for both individuals and legal entities, and good uninterrupted Internet.
NETBYNET
The company began its cooperation with Megafon in 2011. Geographically, the operator is located in seven districts of the Russian Federation: Central, Northwestern Federal District, Southern, Volga, Ural, Far Eastern and North Caucasian Federal Districts. The number of network subscribers is more than 800 thousand.
NETBYNET offers its customers a wide range of services for home and office. These include broadband access to the Internet, telephony, and digital television. There is also a specially developed application for unlimited Internet Wifire TV, which is available on IOS and Android platforms.
NETBYNET in 2021 entered into a contract with MosGorTrans to connect transport infrastructure with Wi-Fi to the Internet for passengers.
Maliciousness of cell towers
Cellular communications is a major breakthrough in the science and technology of its time, which was not without consequences. The cell phone industry continues to claim that cell towers pose no health risks, but fewer people believe this these days.
Are cell towers harmful? Unfortunately, the correct answer is yes. Microwaves can affect your body's electromagnetic fields, causing a variety of potential health problems:
- Headache.
- Memory loss.
- Cardiovascular stress.
- Low sperm count.
- Birth defects.
- Cancer.
There is compelling evidence that electromagnetic radiation from towers is harmful to health.
Example: A study on the effects of a cage tower on a dairy herd was carried out by the government of the state of Bavaria in Germany, the results were published in 1998. The construction of the tower caused adverse health effects, leading to a noticeable drop in milk production. The movement of cattle restored milk production. Moving them back to their original pasture recreated the problem.
Cellular communications in Russia
Of the 100 possible Russian cellular codes, 79 are in use and 21 are free. Free codes are in reserve and do not yet belong to any operator.
More than 80 cellular communication companies are registered in the Russian Federation and provide their services throughout the country. Mobile operators have telephone codes in 9xx format. Mobile phone numbers are ten-digit and start with +79xx or 89xx.
The largest operators include: MTS (Mobile TeleSystems), Beeline (Vympel-Communications), MegaFon, Tele2 (T2-Mobile). The Big Three operators (MTS, Beeline and MegaFon) own entire series of numbers.
Virtual operators working on Tele2 networks
The telecom operator Tele2 was formed in 2001 by the Swedish group Tele2 AB based on network equipment purchased in the Russian Federation. The company provides its services in 60 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The company is successfully developing among leading operators, providing its subscribers with fairly good communications at low prices.
Tele2 is rapidly progressing in the MVNO field. Thus, according to Maxim Mitkin (CEO of the company), there are currently 18 virtual mobile operators operating on Tele2 equipment, which include Rostelecom, Sberbank (Sbermobile), Virgin Connect, MCN Telecom, TTK, Easy4, V- Tell, Tinkoff Mobile and a number of others.
Er-telecom
ER-Telecom (Dom.ru) is a leading independent federal provider of telecommunications services. Provides services such as cable and HD television, broadband Internet access, mobile and landline telephone communications.
Together with the company Tele2, MVNO began working in networks at the end of 2015. But the cooperation was not successful, since the prices for tariffs were not attractive to potential subscribers.
Telephone services were discontinued in September 2021.
Rostelecom
Public company Rostelecom is one of the largest telecommunications companies in the Russian Federation and neighboring Europe. Since 2021 Operates on the Tele2 platform as a virtual provider.
The operator is at the top of the rankings in the domestic market for broadband access services and commercial television broadcasting: the audience of service consumers is 13 million, and Rostelecom’s commercial television is 10 million viewers, of which more than 5 million are viewers of the new media product “Interactive TV”.
Rostelecom is a leading player in the market of telecommunications products for the Russian government and commercial subscribers at all levels.
In July 2021, the number of Rostelecom MVNO users reached 500,000. Rostelecom managed to gain such a base during eight months of MVNO operation on the networks of T2 RTK Holding (Tele2 brand).BBB-”, as well as the Standard & Poor’s agency at the “ BB+.”
SberMobile
SberMobile is a virtual operator that uses the infrastructure of the Tele2 network.
The range of SberMobile tariffs is very diverse. Each subscriber can set up their own tariff based on personal preferences. The most economical one is available at a price of 200 rubles, it includes 150 minutes of calls and 3 GB of network traffic in Russia. The Premium tariff plan includes 1,500 minutes of communication and 30 GB of network traffic, its price is 1,150 rubles per month. There is a limit for free SMS – it is 50 messages. By paying extra, you can get unlimited access to various instant messengers and social networks.
For the company's subscribers who are Sberbank card holders, there is a “Thank you” bonus program. For paying for communications through the bank's app, clients receive cashback of up to 20%. There is also a Wi-Fi calling feature that allows you to stay connected even when the signal is low.
Tinkoff Mobile
This telecom operator began operating in December 2021. Rents a platform from Tele2. Tinkoff Mobile sells SIM cards in more than 15 regions of Russia. Tinkoff Mobile has a number of advantages. For example, a subscriber can set up his own tariff, which is convenient only for him, choosing any number of minutes or gigabytes of Internet.
The operator offers a number of bonuses:
- Several SIM cards can be linked to one account, which is very convenient.
- Owners of plastic cards of the bank of the same name receive cashback of up to 30% for communication payments, and for a positive balance on the card over 1000 rubles - 6% per annum per month.
- Gives 1000 rubles to the account of all new subscribers.
DANYCOM
Ceased to exist.
Communications operator DANYCOM launched in June 2021. The main office is located in Krasnodar. One of the few operators that can boast of a total absence of roaming in Russia. The subscriber card has maximum coverage. Where Tele2 communication does not exist, the operator automatically switches the subscriber to another partner tower. DANYCOM offers its subscribers a “Free” tariff, which allows you to communicate economically.
The operator is a partner with more than 100 communication providers, including at the international level. Thanks to this, calls abroad remain cheap.
TransTeleCom
TransTeleCom began its activities in MVNO in Rostov in 2017.
TTK is one of the top five leading domestic communication operators. The main shareholder of TTK is JSC Russian Railways, the percentage of assets owned is 99.99%. TransTeleCom is a provider of backbone communication services for leading operators and large associations, the range of which extends over more than 78,000 km. The number of TTK subscribers reaches almost 2 million.
TTK has connections with networks of neighboring countries, including China, Finland, the Baltic region and the CIS. This is the optimal route between Europe and Asia.
EASY4
The opening of the Easy4 mobile provider took place in June 2021 at the Startup Village conference for startups in Innovative.
EASY4 SIM cards are equipped with Multi-IMSI technology, that is, several numbers can be recorded on one SIM card. The company offers quite favorable tariffs for its subscribers. The main emphasis is on long-distance communication. Few of EASY4's competitors can boast of free incoming calls in absolutely any country. At the same time, the cost of outgoing calls to other countries is only 2 rubles/min. The price of Internet traffic is 10 kopecks per 1 MB.
Multi-IMSI allows you to choose the connection of any of the Big Four partners with optimal reception and this is an innovation in Russia.
In October 2021, the FSB approved the sale of eSIM with the ability to switch between telecom operators.