What is mobile Internet?
Mobile Internet is a method of wireless access to the Internet. First of all, such access provides the subscriber with freedom of action and mobility - the ability to use communication on any device - from a mobile phone to a laptop.
The advantages of using the mobile Internet today are already more than obvious.
- availability practically throughout the entire territory of Ukraine
- wide possibilities for using video calls, watching videos online and accessing your accounts in mail, social networks and cloud services
- access to the network where there is no wired Internet and there are no other connection options either
- the ability to distribute the Internet to friends
Current trend
What is LTE cellular connectivity on a tablet? Recently, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access based systems such as LTE with frequency reuse 1 have also been deployed.
Since such systems do not propagate the signal across a frequency band, inter-cell radio resource management is important to coordinate the allocation of resources between different cells and to limit inter-cell interference. There are various Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) techniques already defined in the standard.
Coordinated scheduling, multi-site MIMO, or multi-site beamforming are other examples of inter-cell radio resource management that may be standardized in the future.
How does mobile Internet work?
The source of mobile Internet is the signal transmitting antenna. The further you are from the antenna, the weaker the signal. In 3G networks, to protect communications from interruptions while the subscriber is moving, “soft handover” is used - a technology that allows one base station to pick up a client as he moves away from another station.
If you use the mobile Internet of cellular operators, then to access the Internet you can use your own phone, smartphone or communicator. When connecting to the 3G Internet of Intertelecom or TriMob, a separate modem provided by providers is used. The modem receives a signal from the antennas of those operators whose channel it is tuned to. The difference between individual operators is what specific technology they use. and, accordingly, what speed of Internet access is offered. For TriMob, for example, outside the coverage area, 3G communications switch to national roaming and operate at 2G speeds. Intertelecom's connection simply disappears. In this case, the speed of the Internet while moving will be different from that if you were at rest.
3G speed is distributed as follows:
- for subscribers with high speed (up to 120 km/h) - 144 kbit/s
- for subscribers with low speed (up to 3 km/h) - 384 kbit/s
- for stationary objects at short distances - 2 Mbit/s.
Non-voice services of cellular networks.
Cellular network subscribers have access to a whole range of non-voice services, the “range” of which depends on the capabilities of a particular phone and the range of offers of the operator company. The list of services in your home network may differ from the list of services available in roaming.
Services can be communication (providing various forms of communication with other people), informational (for example, reporting on weather forecasts or market quotes), providing access to the Internet, commercial (for paying for various goods and services from phones), entertainment (mobile games, quizzes) , casinos and lotteries) and others (this includes, for example, mobile positioning). Today, more and more services are appearing that are “at the intersection”, for example, most games and lotteries are paid, games using mobile positioning technologies are appearing, etc.
Almost all operators and most modern devices support the following services:
– SMS – Short Message Service – transmission of short text messages;
– MMS – Multimedia Messaging Service – transmission of multimedia messages: photos, videos, etc.;
– automatic roaming;
– identification of the calling subscriber number;
– voice mail – saving voice and text messages transmitted while the subscriber was out of the access area;
– ordering and receiving various means of personalization directly via cellular communication channels;
– access to the Internet and view specialized (WAP) sites;
– downloading ringtones, pictures, information materials from specialized resources;
– data transfer using the built-in modem (it can be carried out using various protocols depending on what technologies a particular device supports).
Mobile Internet in Ukraine - providers
Mobile operators (MTS, Kyivstar, Life) use 2.5 G (GPRS)/2.75 G (EDGE) technologies. The data transfer rate is 30-80 kilobits per second. In some cases up to 150 kilobits. Such Internet costs on average 1 UAH per 1 MB and is quite popular due to the wide coverage of the territory by the operators themselves and the presence of a large number of antennas, including outside the city and on highways. You shouldn’t count on good connection quality and great capabilities of such an Internet, but for viewing your feed on social networks and downloading maps to GPS, this may be enough.
3G communications, although no longer an innovation, are just developing in Ukraine. The standard UMTS/W-CDMA (3Mob) and EVDO Rev.A and EVDO Rev.B (Intertelecom) are common in Ukraine. 3G Internet speed averages from 3.1 Mbit/s when using UMTS/W-CDMA and up to 14.7 Mbit/s using EVDO Rev.B. The quality of 3G network coverage in Ukraine is still weak, but in a large city such Internet will give cellular operators a head start in terms of speed. It is most convenient to use 3G for laptops, tablets or to set up wi-fi in a small company. In Ukraine, 3G Internet is offered by 4 Ukrainian providers: PEOPLEnet, Intertelecom, TriMob, MTS Connect 3G.
Cellular Signal Encoding
To understand what cellular communication is, you need to understand its standards. To distinguish between signals from several different transmitters, the following varieties of multiple access have been developed:
- Time Division Management (TDMA);
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDMA);
- code division (CDMA);
- orthogonal frequency division MA (OFDMA).
In TDMA, the transmit and receive time slots used by different users in each cell are different from each other.
In FDMA, the transmit and receive frequencies used by different users in each cell are different from each other.
The CDMA principle is more complex, but achieves the same result: distributed transceivers can select a single cell and listen to it.
TDMA is used in combination with FDMA or CDMA in a number of systems to provide multiple channels within the coverage area of a single cell.
Mobile Internet tariffs
You can find out about tariffs for mobile Internet on the websites of mobile operators. Tariffs for 3G Internet can be found on the “Providers” page of our website. Typically, all tariffs are divided into unlimited and with a limited amount of traffic. At the same time, the access speed also varies from the minimum to the maximum possible for the technology used. In general, comfortable work with email programs, social networks, cloud services and viewing media files will cost about 150 UAH/month with unlimited traffic.
Broadcasting messages and signals
What is cellular communication? The definition is given above. Almost every such system has some kind of broadcasting mechanism. This can be used directly to distribute information to multiple mobile phones. Cellular communication amplifiers are also used for this purpose.
Typically, for example, in mobile telephony systems, the most important use of broadcast information is to set up channels for one-to-one communication between the mobile transceiver and the base station. This is called a cellular signal. Three different signal application procedures are commonly used: serial, parallel and selective.
The details of the paging process vary somewhat from network to network, but usually the limited number of cells in which the phone is located is known (this group is called a coverage area in a GSM or UMTS system, or a routing area if a packet data session is involved; in LTE, cells are grouped into tracking areas ).
Signaling occurs by sending a broadcast message to all these cells. Signaling messages can be used to convey information. This occurs in pagers, in CDMA systems for sending SMS messages, and in the UMTS system where it allows for low downlink latency on packet connections.
How to connect to mobile Internet?
To use the Internet on a mobile phone, you just need to set up this service on your phone and use the network of the operator whose card you already have installed.
To connect to the 3G mobile Internet service of providers, you need to check the network coverage in the place where you plan to work and only then purchase the equipment necessary for this. To do this, use the provider search service by filling out the selection form on the right , and indicate the point on the map where you need Internet access. Then send a connection request to our operators.
For 3G you need to buy either a USB modem or a mobile wi-fi router and an operator SIM card. The modem can be connected to a laptop, to the cigarette lighter in a car, or even to a desktop computer. The Wi-Fi router works autonomously and does not require a direct connection. At the same time, you can distribute the Internet via wi-fi to 8 more devices. The cost of the modem depends on its functionality and the ability to connect an external antenna to it to strengthen the signal.
You can view 3G equipment and package offers on the “Equipment” page and purchase them in our office.
Concept
What is cellular communication and how does it work? In a cellular radio communication system, the land area to be provided with this service is divided into cells according to a pattern that depends on the characteristics of the terrain and reception. It may be approximately hexagonal, square, circular, or some other regular shape, although hexagonal honeycomb is standard. Each of these cells is assigned a set of frequencies (f1 - f6) that have corresponding radio base stations. A group of frequencies may be reused in other cells, provided that similar frequencies are not reused in adjacent cells as this could cause co-channel interference.
The increased capacity in a cellular network, compared to a single-transmitter network, is due to the mobile switching system developed by Amos Joel of Bell Labs, which allowed multiple subscribers in the same area to use the same frequency when switching calls. If there is one simple transmitter, only one call can be used on any given frequency. Unfortunately, there is inevitably some level of signal interference from other cells that use the same frequency. This means that in a standard FDMA system there must be at least one gap between cells that reuse the same frequency.
Coverage and service areas
The service area of a cell may also change due to interference from transmission systems both in and around it. This is especially true in CDMA based systems. The receiver requires a certain signal-to-noise ratio, and the transmitter must not transmit at too high a power to avoid interfering with other transmitters.
As interference (noise) increases due to increased received power from the transmitter, the signal becomes distorted and eventually becomes unusable. In CDMA based systems, the impact of interference from other mobile transmitters in the same cell on the coverage area is very noticeable.
Examples of cellular coverage can be seen by examining some of the coverage maps provided by real providers on their websites, or by viewing independent crowdsourced maps such as OpenSignal. They show which cellular operator operates in a particular territory. In some cases they may mark the location of the transmitter, in others this can be calculated by determining the point of greatest coverage.
A cell repeater is used to extend the coverage of a cell over large areas. They range from broadband repeaters for home and office use to smart or digital repeaters for industrial needs.
Each cellular provider has its own range of numbers, usually distinguished by code. Using it, you can determine what region and cellular operator the subscriber making the calls has.
How easy is it to start an MVNO?
Now so many companies are launching virtual operators that it seems very easy. So, to open their virtual operator, companies go through a number of stages:
- Preparation. This is the initial stage in which a business plan is prepared. It evaluates the financial capabilities and profitability of the launched project. If there is no client base, then you should consider a strategy for attracting it.
- Conclusion of an agreement. At this stage, you need to decide on the reference operator. You will need to sign an agreement that will stipulate: prices for traffic, obligations of the two parties.
- Billing and equipment. You will need to decide on the billing usage model and equipment. After choosing, sign a lease agreement for the equipment.
- Integration. You will need to integrate with the infrastructure of the selected operator. The process may take 2-3 months. Costs for carrying out are in the range from 2 to 5 million rubles.
- Testing. After all work has been carried out, it is necessary to test the quality of communication. Any errors that occur must be corrected.
- Launch. When working correctly, the operator offers services to citizens.
How is data transferred?
Radio channels utilize the transmission medium efficiently through the use of the following multiple access and multiplexing schemes:
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDMA);
- Time Division Management (TDMA);
- code division (CDMA);
- with spatial division (SDMA).
Small cells, which have a smaller coverage area than base stations, are classified as follows:
- Microcell - less than 2 kilometers.
- Picocell - less than 200 meters.
- Femtocell - about 10 meters.
What is cellular communication for children? This term usually refers to special “children’s” tariffs with special service packages.
Virtual telecom operators - what are they?
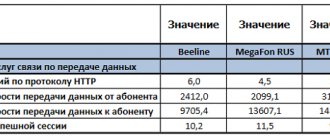
The Russian mobile communications market is divided by 4 large companies: Beeline, MTS, Megafon, Tele2.
“Moving” the big four and winning back part of the market is an impossible task. This will require a large amount of resources - not only money, but also administrative connections. Small companies are forced to compete in the “virtual” field. They purchase network resources from large companies - representatives of the Big Four - and use their infrastructure to sell their services. Statistics for 2021 show the following: the number of subscribers who use the services of virtual operators in Russia is 6 million people. Was involved in data collection.
Some companies use MVNOs to further monetize their customer base. A good example is Rostelecom, Tinkoff Mobile, VTB Mobile and others. At first glance, it may seem that it is not profitable for mobile operators to breed competitors and provide them with infrastructure for development. In practice, in such a scheme, representatives of the Big Four do not need to spend their own resources on attracting new clients.
Why "virtual"?
In modern conditions, it is almost impossible to create a “real” cellular operator for any money.
It all comes down to licenses for the corresponding frequency ranges and communication technologies, which become the object of division at the highest level. At the same time, administrative resources are being used left and right - just remember the “Swedish” Tele2, which, contrary to all logic, never received a 4G license. So in the foreseeable future, no one else will be able to repeat the success of Rostelecom, which turned the “Big Three” into the “Four” - almost all the small regional players have already been taken over and absorbed. There is no place for newcomers - a “natural oligopoly” has arisen. Therefore, those who, for one reason or another, want to provide services under their own brand are forced to buy network resources from one of the market owners. Often - together with a personal account and billing.
Fifth generation of mobile communications (5G)
Pre-commercial and commercial launches of networks are currently underway. More information about the launches of 5G networks in Russia and the world can be found at the corresponding links.
The following requirements are stated for fifth generation networks (in comparison with LTE):
— 10-100 times increase in data transfer speed per subscriber;
— Increase by 1000 times the average traffic consumed by a subscriber per month;
— Ability to service a larger (100 times) number of devices connected to the network;
— Multiple reduction in energy consumption of subscriber devices;
— Reduction of network delays by 5 or more times;
— Reducing the overall cost of operating fifth generation networks.
Requirements for 5G networks in digitized form are presented here.
For more detailed information about the evolution of mobile communication networks, the current state, trends and prospects for its development, read the latest reference book “Mobile communications on the way to 6G”.
Video: choosing the best mobile operator
Author: Mobilniy Operator
04-07-2017
(6)
Mobilniy Operator
SIMILAR ARTICLESMORE FROM THE AUTHOR
MOBILE TIPS
Is it possible and how to find a person by phone number?
MOBILE TIPS
How to determine the country of origin of a phone using IMEI
MOBILE TIPS
What to do if your iPhone is frozen: ways to reboot
LEAVE A COMMENT Cancel reply
GSM network architecture
The most common example of a cellular network is a mobile (cellular) telephone network. It is a portable telephone that receives or makes calls through a cellular station (base) or transmission tower. Radio waves are used to transmit signals to or from a mobile phone.
Modern cellular networks use cells because radio frequencies are a limited shared resource. Cellular stations and telephones change frequencies under computer control and use low-power transmitters so that a typically limited number of radio frequencies can be used simultaneously by many subscribers with less interference.
How to increase the Internet speed of Yota 4G, Megafon, MTS and Beeline?
Let's first talk about the popular Iota. In order to correct this sad situation, it is necessary:
- Go to “Settings > SIM cards and mobile networks > Operator name (Yota, Megafon, MTS, Beeline) > Access points > Operator name
and select “LTE” or “4G” as the data transfer standard in the “Owner” section
Next, we go to the access point settings and register client.yota.ru as the APN, instead of yota.ru, internet.megafon.ru instead of internet for Megafon, client.mts.ru instead of internet.mts.ru for MTS, home.beeline. ru for Beeline - incorrect values could be set when automatically receiving settings from the operator.
Since Yota is a virtual operator, for it we change the “MVNO Type” to IMSI. For other operators, nothing needs to be specified in this paragraph. Then save the settings and reboot the phone.
How to switch to a virtual operator and what you need to consider
Becoming a subscriber to a virtual operator is simple - for the client the process is no different from connecting to a regular operator. To do this you will need:
- Contact the selected operator;
- Apply for a SIM card.
- Sign the agreement and receive the card.
It is important to consider that you can make the transition while maintaining the number
(using MNP technology). To do this, you will need to write an application, which will be provided by an employee of the communication salon. This can cost up to 100 rubles.
When changing operators, as always, you need to take into account some subtleties:
- When choosing a little-known company, you should carefully study the information about it in order to avoid fraud.
- Virtual operators may have lower rates because they assess the needs of “niche” clients.
- When paying for services or goods via phone, all data can go to the selected operator.
Little-known companies or fly-by-night companies can collect data or sell. It is also possible that the data obtained will be used for the purpose of fraud.
Virtual operators by type
Large banks and companies are launching their own telecom operators because certain types of businesses need them. As a result, they were divided by industry.
The main types of virtual operators are:
- Light MVNO is the simplest solution, without serious obligations, most of the work remains with the core operator. Such operators earn money from dealer commissions. This is an excellent option for those who want to isolate themselves from technical issues.
- Pro MVNO - such a network provides great opportunities and is suitable for those who have their own billing and other technical capabilities. In this case, an agreement is signed, and the new operator decides which payment system to choose (in advance or after the provision of services), how to provide customer support, and what tariffs to offer.
- Full MVNO is a model for corporate clients (owners of mobile payment systems or telecom operators). In this case, the operator receives a full range of possibilities, including assigning numbers.