TTL (Time To Live) is the time value during which a data packet wanders through the network with the ability to transfer information between servers and individual devices. After this time, the data simply disappears without determining whether it has reached its end point or not. This function allows you to limit certain transitions and allows you to establish system security. Today we want to talk about changing this value on a local computer running the Windows 7 operating system, having first examined the very purpose of this operation.
Expand TTL value Asus - what is it?
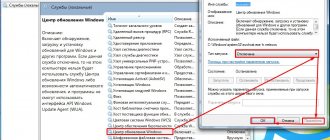
On routers from Asus, Zyxel and other companies you can find two settings:
- Extend The TTL Value is an option on the router that works for incoming traffic; if a packet with a TTL of 1 comes from the provider, it will not be reset. As a result, all your internal devices will be able to receive it.
- Change the LAN TTL value - needed to send packets with a fixed TTL, regardless of how many nodes are on the local network, the TTL will still be the same and the provider will not block you.
These are the options in the router settings:
Is it possible to edit TTL without root rights
You can change TTL without these rights, but not on every device running Android. You should install the Terminal Emulator for Android application on your gadget.
After installing the program you must:
- Activate the application and type the following combination - cat / proс / sys / net / ipv4 / ip_default_ttl.
- If the device model allows you to make adjustments without administrator rights, then the original TTL indicator will become available. You need to increase it by one. The same change must be made in all devices connected to the network.
We recommend: How to delete contacts from an Android smartphone
- Reboot all equipment and then evaluate the result.
Although this method works, it is effective in rare cases. Therefore, it would be more reliable to obtain root rights and be guaranteed to bypass traffic restrictions by the provider.
Why are these settings needed?
Both of these options are designed to simplify work when using the mobile Internet when there is a limit on the number of connected devices.
It turns out that the mobile operator can limit the distribution of the Internet, that is, when you bought a modem and connected it to the router so that it distributes the Internet, for example, via Wi-Fi (or the modem has such a function initially)... and the operator does not like it. He wants only one person to use his Internet (economically logical). The provider can analyze the TTL to determine whether the user has a router or not, and if so, the Internet may be blocked. But the options discussed above may prevent him from doing this.
But in general, it’s rare for a provider to suffer from such nonsense, but there have been cases.
TTL has changed, but I can’t download files
There is another important nuance that users are periodically perplexed by: there is a connection, there is no blocking from the operator, but there is no speed at all. This usually happens in situations where the user tries to access sites that are blocked by the operator for one reason or another.
For example, in most cases, users are unable to log in and download files from sites associated with torrent trackers, online casinos that are not licensed in the Russian Federation, and so on. It is not yet possible to bypass such blocking on the part of the user.
You can check whether the site is blocked by the operator or not in the Roskomnadzor register
If the user does not want to pay for distributing mobile traffic to his PC, he needs to take care of changing several parameters on his computer, the list of which includes changing the TTL value (should be 64 instead of 128), the contents of the “hosts” file in the Windows root folder and disabling automatic updating of the operating system along with the presence of account administrator rights.
TTL - what is it anyway?
It stands for Time To Live and means the lifetime of the packet.
The Internet is transmitted in packets, for example, from a laptop to a phone or vice versa; packets containing data are constantly sent. And each packet has a value called TTL - the packet lifetime in the IP protocol .
The default TTL is different for each device. Each time the device passes through, the TTL of the packet decreases by one. The device can be a modem, phone, router, or other network equipment. If the TTL was initially equal to 128, then, for example, if the packet passed through the modem, then it will be 127 (minus one).
A mobile operator, if it wants to understand whether a router is being used or not, can analyze the TTL value of packets that come from the subscriber. For example, if only a smartphone is used, then the packets come with TTL 128, and if a router is used, then it will already be TTL 127. As a result, the operator sees that the TTL is jumping and concludes that they are surfing the Internet not only from the phone, but also from other devices, then There is a distribution of the Internet, and this costs an additional fee. But of course not all operators have this.
Smartphones on iOS and Android have a TTL of 64, and in Windows - 128.
How to find out the host operating system by ping
Good afternoon, dear blog readers, today I want to ask you, can you use the ping command to determine which device or operating system is responding to you? If not, then you have come to the right place and I will tell you another purpose of the ping utility. I think this material will be useful for both beginners and advanced users, especially when you are looking for the cause of a malfunction in a network or service, I have seen many times that you think that one server is answering you, but in fact it is another, because someone , I changed something and didn’t document it.
TTL value
Earlier I told you about the OSI model, and there a network packet has such a TTL (Time To Life) value, if translated, this is the lifetime of the packet. TTL is a kind of counter that decreases by one when a network packet or, as it is also called, a frame passes through a router; this is done so that, if it is impossible to find a destination, it does not constantly run around routers, creating load and spurious traffic.
It is the packet lifetime (TTL) that will help us determine who is on the other side. Each operating system has its own indicator, for example
- Cisco TTL > equal to 255
- ttl windows > equal to 128
- Unix ttl > equal to 64
- Android and IOS Apple>65
- Lumia > 130
As you can see, it’s different for everyone, and let’s figure it out, for example, I’ll ping a Cisco switch, for this we open the Windows command line, you may also have Linux.
We write ping 10.152.1.1 (you may have a different address)
As you can see, the ttl value here is 255, which shows that the IOS of the Cisco device is responding to you, as you can see, the ping command perfectly recognized the host operating system on the other side.
Let's try to ping a Unix system, for example, on my local network, the gateway is Kerio Control, on the Linux version. Let's ping.
We write ping 192.168.5.1 (you may have a different address)
As you can see here, the ttl value is 64, which means a unix platform, so various D-link devices and other home routers can respond.
Let's also check the windows of the platform, for example, I have Windows 8.1 on the local network, let's do a ping. And you see that it is equal to 128, just like I said.
There you are. then the mystery is, we ping Windows Server 2012 R2, it has a website relay.aetp.ru. What do you see, the ttl value is 120, but in windows 128 is the default, it doesn’t fit