Definition
What is TTL? The term "time to live" refers to the amount of time or "hops" a packet takes to establish itself on the network before being dropped by the router. The technology is also used in other contexts, including CDN caching and DNS caching.
TTL is a value in an IP protocol packet that tells the network router whether the packet was too long. In IPv6, the field in each packet has been renamed. TTL is set in the eighth binary bit in the packet header and is used to prevent packets from endlessly propagating across the Internet or another network. When forwarding an IP packet, routers must reduce the TTL by at least one order of magnitude. If the packet's field reaches zero, the router that detects it discards the packet and sends an ICMP (Internet Control Protocol) message back to the originating host.
Windows 7, 8, 10
The operator's servers have gone further and now track not only TTL, but also block users who connect to dubious servers. If the operator sees that you are connecting to a server that is always used on the computer, then you will be blocked. One such server is the Windows update cloud. So let's disable this feature for now:
Now we turn on distribution from the phone to the PC and check.
How does the technology work?
When a packet of information is created and sent over the Internet, there is a risk that it will continue to move from router to router indefinitely. To reduce this possibility, packages are created with an expiration date called a time-to-live limit. The TTL packet can also be useful in determining how long it has been in circulation and allows the sender to obtain information about the packet's path over the Internet. Each packet has a place where it stores a numeric value that determines how long it should continue to travel through the network. Every time a router receives a packet, it subtracts one value from the TTL count and then forwards it to the next location on the network. If at any time the TTL counter is zero after subtraction, the router will discard the packet and send the ICMP message back to the originating host.
Detailed setting
If there are a lot of programs running on your computer that work with the Internet, and you need them, then when they are running, the operator will block you. For example, you want to use a torrent. When you make a request to the server, the operator will see this and block you. But we can deceive him and simply not send this information. To do this you need to do the following:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
What do these settings do? You may have noticed that there are a lot of links there with the name “Microsoft” - these are Windows update servers. IP 127.0.0.1 is essentially the address of your own computer, that is, if it starts updating Windows, the system will start contacting itself, and not the remote server, but the operator will not receive information. Now the problem is that not all servers are in this file. But you can easily add them yourself.
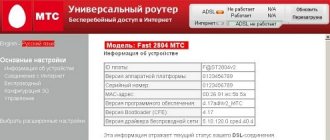
First I'll tell you a simple example. Here you are distributing the Internet from your phone to your PC, and suddenly your operator blocks you. Using the Acrylic DNS Proxy program, you see the address of the server with which you are being blocked. You add this server to the hosts file. And now everything is the same, but with more detailed instructions:
Technical description of the process
The IP TTL is set initially by the system sending the packet. It can be placed at any value from 1 to 255. Different operating systems set different default values. Each router that receives the packet subtracts at least 1 from the count. If the counter remains greater than 0, the router forwards the packet, otherwise it discards it and sends an Internet Control Protocol (ICMP) message back to the originating host, which may cause a retransmission.
The TTL/hop limit point must maintain a continuous flow of packets stuck in routing loops (possibly due to incorrect data tables and network congestion). In Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) clouds, the TTL is copied from the IP TTL when an IP packet enters the cloud. On exit, the MPLS TTL value is copied into the corresponding field as long as it is less than the value in the field.
Fast way
You can change the TTL programmatically; for this you need to download a special TTL patch. I posted it so you can download it here.
I tested this patch on my Windows 7 computer, changing the value to 65 - everything worked.
Just run the file as administrator and enter the value 65 in the field. And then, just in case, restart your computer.
Changing TTL using a patch
I can’t say that this is the best and safest way, but so far everything seems to be ok, the computer hasn’t exploded.
This method is the fastest.
I hope you understand how to change TTL on Windows and why to do it.
Source
Changing TTL
The ping and traceroute utilities use the TTL value to try to reach a given host computer or trace a route to that host. Traceroute sends a stream of packets with successively higher TTLs, so each will be dropped in turn by the next hop (router) on the way to its destination: the first packet has a TTL of one and is dropped by the first router, the second has a TTL of two and is dropped by the next router. The time between sending the packet and receiving the ICMP response message is used to calculate each subsequent travel time.
In IP multicast, the TTL controls the area or range within which a packet can be forwarded. Conventionally, IP is limited to:
- 0 — host;
- 1 - subnet;
- 32 - website;
- 64 - by region;
- 128 - continent;
- 255 - unlimited.
Change the Time To Live setting on your computer
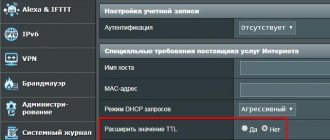
Some mobile operators want the user to access the Internet only from one mobile device from their network. Subscribers often turn on an access point and distribute the Internet to other home devices with Wi-Fi. The operator sees this by analyzing TTL data and can block access temporarily to clarify the circumstances or require additional payment for the service.
To get around this, you can configure your computer to be recognized by your carrier as a mobile device. Our task is to make the TTL of the computer (128) equal to the value of the mobile device (64). One more detail is important here. If the phone distributes the Internet to other devices, then it is already considered one of the nodes for the TTL computer. Therefore, when changing this parameter on a PC, you need to set it to 65, not 64.
To do this, change some Windows registry settings:
- Open the input line by pressing two keys simultaneously WIN+R.
- Enter the following command: “regedit”.
- In front of you you will see the Windows registry, here you will find the “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE” section.
- Then select the “SYSTEM” branch, below, select “CurrentControlSet” with the pointer.
- In the branch that opens, select “Services”, “Tcpip”.
- And select the last folder "Parameters".
- In this branch you can edit the parameters of the transmitted data packet. Here we need to create a new parameter and enter its name “DefaultTTL”. To do this, right-click (right mouse button) on the left block and select “Create”, to the right click “DWORD32 Parameter”.
- This is where you need to enter the values for the TTL of the computer. Enter 65 here. Select "Decimal" number system.
If you change settings in Windows 7, 8.1, then you need to do the same for the “Tcpip6” branch. The remaining points remain the same. Once you have configured the settings you want, close the registry and restart your computer. Now your computer will be identified by operators as a mobile device, and you, in turn, will worry-free use the Internet from all home devices.
This may be useful: Control userpasswords2 does not work on Windows.
TTL and DNS caching
What is TTL in the context of DNS? The value tells local servers how long a record should be kept locally before a new copy of the record is restored from DNS. The storage of records is known as a DNS cache, and the act of storing records is called caching.
The term "time to live" is also used to describe the time it takes for a DNS entry to be returned from the cache. In this context, the USB TTL is a numeric value set in the DNS entry on the authoritative DNS server for a domain that determines the number of seconds in which the cache server can provide its value for the entry. When the required number of seconds have passed since the last update, the caching server will contact the server again and get the current (and possibly changed) value to write. Characteristics of the caching process, where TTL:
- It is part of the domain name system.
- Set by the authoritative name server for each resource record.
- Used for caching purposes. For example, the TTL value for www.dnsknowledge.com is 86400 seconds (24 hours). The higher the TTL of the record, the longer the information will be cached and the fewer queries the client will have to make to find the domain.
- Used by the name resolver to speed up the resolution by caching the results locally.
Checking superuser rights on a smartphone
To change the “lifetime” value of an Android device, you must obtain administrator rights (root rights). Additional software will help with this, which can be downloaded for free on Google Play. Popular applications such as Root Checker or Terminal Emulator will allow you to determine your existing superuser rights. The interface of the first application is very simple and allows you to check intuitively. When using the second one, you must enter “SU” in the command line, which will help determine whether you have root rights. The # or $ icons shown will confirm a positive result.
TTL - what is it and how does it work?
In HTTP, time to live represents the number of seconds that cached web content can be returned before a server request. The default value is determined by settings on the web server, but can be overridden by cache control tags that control which types of servers can cache data.
A packet is a fundamental unit of information transport in all modern computer networks and other communication networks. A router is an electronic device or network layer software that connects local or wide area networks and forwards packets between them.
Application cases
In addition to tracing packet routes across the Internet, TTL is used in the context of caching information over a period of time. Instead of measuring time between routers, each of which can take a certain number of hours, some network use cases work in a more traditional way.
A CDN typically uses TTL PL to determine how long cached content must be served from the edge CDN server before a new copy is fetched from the origin server. By properly setting the time between origin server loads, the CDN can serve updated content without continuously propagating requests to the origin. This optimization allows the CDN to efficiently serve content closer to the user, reducing the required bandwidth from the origin.
In the context of a DNS record, the TTL is a numeric value that determines how long the DNS cache server can serve the record before contacting the authoritative DNS server and getting a new copy of the record.
Lockdown has arrived again
Quite recently it became known that the TTL value of MTS was changed. Therefore, go to the registry again in the previous way and instead of 65, set the value to 64. For those who have an MTS operator, this method works, but for others, this method may also work, so try it.
As I said earlier, the operator will monitor which servers you access. If you have a system update enabled, your antivirus has started updating, you are downloading from a torrent, or Steam is turned on, then the operator will see this and block you. Therefore, there are three options: