Many mobile operators in Russia develop their tariff packages exclusively for a certain area. And as soon as the subscriber leaves this area, roaming is activated for him. Of course, there are tariff packages that apply without changes throughout the country. And as a rule, such services cost much more and are beneficial if you often leave your region. But for those who rarely travel outside their region, the mobile communications company MTS has developed special tariffs.
MTS intranet roaming 2021: communication services when traveling around Russia
The cellular operator Mobile TeleSystems canceled MTS intranet roaming in Russia back in 2021. However, there has been a little confusion with calls and SMS, because now during a trip the region where the subscriber is currently located (the region of residence) is considered home, and calls within this territory become local for him. And calls to the real home network where the connection took place become long-distance.
The costs of calls and SMS when traveling in Russia depend on the tariff plan. If local packages are connected, then when traveling they will only be valid within the region of your stay, and calls and SMS outside of it will be considered intercity. If you have connected packages that are valid throughout Russia, you can safely continue to communicate while traveling under the same conditions.
with mobile Internet is simpler - since 2018 it has been operating throughout the country without additional payments. While traveling around Russia, subscribers can communicate via instant messengers and use social networks under the same conditions as at home.
Tariffs without surcharges when traveling around Russia
The mobile operator MTS has a number of tariffs that allow you to use cellular communications when traveling around the country under the same conditions as at home. Having chosen one of them, you don’t have to think about the costs, they won’t change. These tariff plans include:
- “Tariff” - includes from 600 to 1600 minutes and SMS to all Russian networks and unlimited Internet (25 GB of traffic). Monthly payment – from 525 to 1075 rubles. (the amount depends on the selected package of minutes and SMS).
- “ULTRA” – 3500 minutes within Russia, 3500 SMS within Russia, unlimited Internet (15 GB of traffic) for 1800 rubles. per month.
- “Smart Top” - 2000 minutes to all networks, unlimited calls to MTS numbers throughout Russia and unlimited Internet for 1300 rubles. per month.
All other MTS tariff plans provide for a change in tariffs when a subscriber moves to another region of the Russian Federation.
A guide for the novice roamer
Many owners of mobile phones had to travel abroad or at least outside their region. Some go on vacation to the south once a year, others often go on business trips, and some travel constantly. In this case, a situation inevitably arises when a phone connected to one operator is serviced in the network of another operator - roaming (from the English roaming - wandering). In Russia, there is the concept of intranet roaming: using your operator’s network outside your home zone. In both cases, it is not the terms of the tariff plan that apply, but the prices set by the guest operator. Roamers will have to forget about all sorts of “favorite” numbers, free incoming calls from mobile phones (including on-network), per-second billing, “preferential” time, “free” minutes provided for a certain monthly fee and other amenities available only on the home network. Even checking your balance (with the exception of USSD requests) and calling customer service will be charged.
However, many subscribers use their phone in roaming in the same mode as at home. This leads to quite significant sums being written off from the account, the disappearance of which is often attributed to the “theft” of the operators. However, roaming is a very convenient and useful service that allows you to stay connected while traveling and spend quite reasonable money if done correctly. We will limit ourselves to considering roaming in the GSM standard, since other standards (DAMPS, CDMA) are less common in Russia and in the world, and roaming in them, although possible, is often difficult.
Before you leave:
1. Make sure that your tariff plan includes roaming service. There are tariffs for which roaming is not available or is limited (for example, the Megafon-Lite family in some regions). In this case, you can change your tariff plan or get another connection to the same or another operator. In this case, you will receive another number, which you can give only to the right people, or you can forward it to it from the old one. If they often call you on a regular number, without knowing that you are in roaming, there is a risk of spending a large amount.
In every major city in Russia and the CIS there are from two to five GSM operators. For traveling around the country, it is preferable to connect to large national operators that have a developed network in the regions (in Russia these are MTS, Bee Line and Megafon, in Ukraine - UMC and Kyivstar), and for traveling abroad it is better to choose an operator with the most favorable prices for international roaming .
For frequent trips, it is advisable to choose a tariff without a monthly fee (or with the lowest monthly fee) and without prepaid traffic - so that under normal conditions, telephone costs are minimal or non-existent. The cost of calls on your home network is not important: roaming prices do not depend on the tariff plan. The ideal tariffs are “Super-Jeans”, “Jeans-007” (MTS) and “Bi+Time”, “Bi+Boom” (Bee Line): there are no mandatory payments and no restrictions on the payment period, only fee for caller ID, which you don’t have to use. The only condition: at least once every six months you must make a charged call or send an SMS, otherwise the operator has the right to terminate the service contract.
2. If you intend to travel without leaving Russia - for example, to go to a neighboring region or on vacation in Sochi, you can limit yourself to intranet roaming. You just need to check with the help desk or on the operator’s website whether it operates in the desired city. For Bee Line and MTS subscribers, intranet roaming is enabled by default.
In addition to intranet, there is national (across Russia) and international roaming. To activate “full” roaming, MTS subscribers need to visit the subscriber department and write an application, and in Bee Line (users of “Bi+” tariffs) it is enough to deposit an amount exceeding 50 USD into their account. Other operators have different roaming connection conditions: check them with the help desk or subscriber department. Make sure that there is a sufficient amount in the account: the money may suddenly run out as soon as the operator receives bills for roaming (which does not happen immediately: in particularly advanced cases, bills can take 1-2 months), and top up the balance outside your region and Moreover, it is very problematic abroad.
3. It is desirable that the operator provides the ability to manage a personal account and services via the Internet. In MTS this can be done by ISSA (Internet subscriber service system), in Bee Line - beeoffice, in Megafon - “Service Guide”. Be sure to activate these services and set a password for access! This can only be done while in the home zone.
To avoid charging problems outside your home network, disable all unnecessary additional services, primarily voicemail, conference calling, call waiting and call hold. It is advisable to leave only Caller ID (automatic number identification) and, if necessary, data transfer. When roaming, you need to use forwarding with great care. If call forwarding is set to “busy” (the phone will be “busy” if you press the “hang up” key without answering the call), no answer (the subscriber does not answer the phone) or unreachability (the phone is turned off or out of network coverage) to voicemail or to another number, then you risk paying twice! If the phone was not turned off, but lost the network, the call will be directed to the network in which the phone was last registered and then forwarded. In this case, you will be charged for a call to your place of stay and for an outgoing call at the rates of the guest operator, and you will not even suspect it until you see the invoice. As a last resort, you can set up unconditional forwarding or unavailable forwarding, and then be sure to turn off the phone. In this case, you will only pay for a call from your city to the number to which call forwarding is set.
4. Find out which operators operate in the city or country you are traveling to, which of them your operator has a roaming agreement with, and whose tariffs are the most favorable. You can find out about the coverage area of GSM operators, for example, here (however, the information there is very approximate), or on the websites of the operators themselves. Information about roaming tariffs must be provided by your operator: it is recommended that you print them out and take them with you. The most detailed information, along with links to the websites of other operators, is contained on the MTS website, which is worth a look even if you are not a subscriber of this company.
5. If you plan to travel outside the former USSR, you need to purchase special adapters and/or chargers for foreign electrical networks, having found out in advance what voltage and sockets they use. To travel to North and South America, you also need a phone operating in the GSM-1900 or GSM-850/1900 standard. Regular dual-band handsets (GSM-900/1800) will work without problems in Europe, most of Asia and Africa, but they are useless in America. However, there are many tri-band (GSM-900/1800/1900) phone models. In Japan, South Korea and some South American countries, you can rent a local phone and insert your SIM card into it, but if you plan to stay in these countries for a long time, it is easier and cheaper to purchase a phone locally.
Roaming: how it works
Roaming in a guest network is possible only if there is a special agreement between operators. If there is no such agreement, or the roaming service is not activated, then the phone will not be able to register on the network. In the home zone (for Moscow this is the Moscow and neighboring regions, for St. Petersburg - the North-Western region, abroad - as a rule, the entire territory of the country) roaming in other networks is impossible, and outside it it is possible to use the services of several networks at once.
When you turn on or come within range of any network, the phone starts searching for the network. If the network in which the phone was last registered is not detected, then registration occurs in the network with the highest signal strength (in automatic search mode), or you are asked to select a network from the list (manual mode). It is recommended to set the automatic search mode so that each time the phone detects a network, it does not ask permission to register in it, but after that, perform a manual search and, if possible, select the network with the most favorable prices. For example, in the Penza region there are three GSM operators: SMARTS, Megafon and Bee Line. An MTS subscriber can choose two networks - SMARTS and Megafon (roaming in Bee Line is prohibited). Incoming calls from both operators cost approximately the same - 0.85 USD. excluding VAT in Megafon and 0.81 in SMARTS. But a local outgoing call in Megafon costs 1.56 USD, and in SMARTS it costs only 0.55. But the free threshold for outgoing calls in Megafon is 10 seconds (you can talk in intervals of 9 seconds or ask to be called back). And in some places, for example, at the junction of small European countries, you can find yourself in the coverage area of a dozen or more different cellular networks!
Networks are divided into home (home), forbidden (forbidden), preferred (preferred) and available (available). The home network is the network of the “native” operator, and if it is available, it is advisable to register with it: in this case, uniform and relatively low intranet roaming prices will apply, compared to other operators. You can try to register in all networks - sometimes the “forbidden” network allows roaming, while the “available” one remains inaccessible. Thus, Moscow MTS subscribers, while in St. Petersburg, can register both in the MTS network and in Megafon, despite the fact that Megafon is a prohibited network in the home zone. You can set preferred networks so that the phone “sticks” to them first and does not jump to other available networks. For the above example of roaming in St. Petersburg, it is advisable to set the MTS network as the preferred one, since calls to the Megafon network will cost much more.
Depending on the phone model, the MTS network can be recognized as MTS, RUS MTS, MTS RUS (in Belarus - 257 02, BY 02, MTS BY); Megafon - like MegaFon, MEGAFON, NWGSM, RUS NWGSM, North-West GSM, etc. Sometimes instead of the network name you can see numbers: 250 03, RUS 19, CC 250 NC 20, etc. This means that in the firmware (software) of the phone there is no information about this operator (which does not prevent the phone from working in this network), and the screen displays not the name of the operator, but the network code. Each GSM network has its own five-digit code (not to be confused with the telephone code!) The first three digits (CC, country code) are the country code, the last two (NC, network code) are the operator code. Thus, the SS of Russia - 250, Ukraine - 255, Belarus - 257; CC 250 NC 01 - MTS, 02 - Megafon, 99 - Bee Line). Sometimes an SPN (service provider name) is written on the SIM card - a logo displayed on the display instead of a network code: for example, Jeans (MTS) subscribers see the inscription “MTS RUS”, regardless of the phone model and its firmware. On some phones, the SPN is also visible when roaming in other networks next to the name of the guest network.
If the phone cannot register in any network (in this case, instead of the operator’s name, the inscription “SOS only”, “112 only”, “SOS only”, etc. appears on the screen), then, as a rule, you can call for free number 112. Depending on the operator, the call will be directed to the rescue service, police/police or helpline. Calls to 112 are possible even in the absence of a SIM card and from a locked keyboard.
The largest service area in Russia is MTS. In the regions in which the network of MTS and its subsidiaries operates, as a rule, communications are available in all major cities and on highways. In addition to Russia, the MTS network operates in Belarus and Ukraine (UMC). The MTS website has very detailed large-scale coverage maps. The MTS network has a unified payment acceptance system and “federal” payment cards that allow you to pay for a phone in almost all regions where MTS operates. The disadvantage of MTS intranet roaming is the different cost of calls to the regional/regional center and beyond. Outgoing calls to the region in roaming cost 20 cents more than a call to the regional center, even if the subscriber calls to the city in which he is currently located! And calls to any federal numbers of other operators are charged at the maximum rate - 0.74 USD. At the same time, calls to any MTS phone cost only 19 cents, incoming calls (including incoming calls from MTS) and outgoing local calls cost 29 cents.
Bee Line coverage is comparable to MTS coverage in the Central region and Western Siberia and significantly exceeds it in the Caucasus and Volga region (data as of early 2005). However, Bee Line only recently began operating in the north-west of Russia and the Urals, and is completely absent in Eastern Siberia and the Far East. The coverage maps on the website are less detailed and do not always correspond to reality - sometimes they only show the planned coverage. Another disadvantage of Bee Line: the need to have 50 USD. on the account for connecting national and international roaming. With a smaller amount on the account, the phone will be able to register only in the Bee Line network, as well as in the Kyivstar (Ukraine) and Turkcell (Turkey) networks. Roaming is disabled when the account balance drops to 20 USD. The undoubted advantages of Bee Line include the availability of GPRS throughout almost the entire coverage area, as well as unified “Bi+” payment cards throughout Russia.
The third operator, Megafon, works well in the North-West region, the Volga region, the Urals and the Caucasus. In other places, Megafon's coverage is still very limited. Unified payment cards appeared quite recently and are not sold in all regions, so problems may arise with account replenishment. There are also no uniform help desk numbers: if in MTS and Bee Line, by dialing 0890 and 0611 (or 0622), respectively, you can contact a local call center for free (which, if necessary, can switch to a subscriber service in your city), then in Megafon such there is no possibility. A distinctive feature of Megafon is its roaming-free space within one licensed zone (for example, the Volga region or the Urals). Thus, a Megafon subscriber, having left for a neighboring region, does not fall into roaming, like MTS or Bee Line subscribers, but continues to use the phone at the same tariff and under the same conditions as at home. In other licensed zones, intranet roaming operates, and the cost of all incoming and outgoing calls within Russia in this case is the same - 25 cents + VAT.
Intranet roaming is also available in the networks of large regional operators: SMARTS, covering almost the entire Volga region from Yaroslavl to Astrakhan; Tele 2.
Regardless of where the subscriber is located, his phone number remains unchanged, and you can call him in the same way as if the called subscriber was in his own city. Each “federal” code (903xx, 910xx, etc.) corresponds to a specific region and operator, and calls to it are paid in the same way as to landline numbers, that is, free from the “home” city, and from other places - as intercity In some countries, including CIS countries (Ukraine, Kazakhstan), calls to cell phones from regular phones are paid, regardless of where the subscriber is located, but incoming calls to cell phones are free.
Dialing rules vary from network to network. Sometimes you can call your host city without a code, but most often it is required. The common dialing format is + [country code] [city code] [number]. In case of a call to Moscow: +7 095 xxxxxxxx, to Kyiv: +380 44 xxxxxxxx. It is recommended to store numbers in the phone's address book in international format (via “+7”, not “8”), especially since to send an SMS the number must be entered this way. However, in some CIS countries it is advisable to dial numbers in the traditional way: 8?10-[country code] - this can be much cheaper. Thus, the operator Geocell (Georgia) charges calls to numbers dialed through + [country code] almost 5 times more expensive than calls dialed through 8?10! And some operators allow you to call using IP telephony at lower rates - in this case, the dialing rules differ from those indicated above.
In roaming, all calls are much more expensive than at home, and incoming calls are paid at long-distance rates. All calls will be charged only per minute, that is, for a conversation lasting 1 minute. 1 sec. They'll charge you two minutes. Therefore, it is not cheap for subscribers of the same company located in the same place to call each other: one will pay for a call home, and the other will pay for an incoming one. The cost of an incoming call consists of two parts: the cost of a call from the city in which you are connected to the place where you are (according to the tariffs of your operator) and the cost of an incoming call according to the tariffs of the guest network. Foreign operators, as a rule, do not charge money for incoming calls (exceptions are rare), so it makes no difference which network you register with for incoming calls: You only pay your operator for call delivery. But in Russia and Ukraine, depending on the choice of network, the cost of an incoming call may differ several times!
As for outgoing calls, you can get good money with them. For example, in Spain and some other European countries, in addition to the usual per-minute tariff, a connection fee is charged, which will be charged even if the called subscriber has not picked up the phone or is unavailable. In the US and Canada, the call time is counted from the moment the call is made, not from the moment it is connected.
When calling local cellular networks, it makes sense to choose exactly the network whose subscriber you are calling: calls to subscribers of other networks can cost much more. Free thresholds in each network are different and can vary from 3 to 10 seconds, or be absent. But you shouldn’t trust the meter readings on your phone - billing is carried out solely on the basis of the switch data, and it can count that you’ve talked a second more and charge you for a full minute. In the case when incoming calls are significantly more expensive than outgoing ones, you can “bounce” calls and call back to the specified numbers.
To avoid unnecessary costs, you can communicate via SMS or temporarily connect to a local operator (see below). All GSM operators support the ability to send SMS (short message service) - text messages to other phones, not only from handsets, but also via the Internet, by e-mail and ICQ. Unlike a call, the cost of which in roaming can reach 1-2 dollars, an SMS will cost 5-20 cents. Incoming SMS is usually free (exceptions are extremely rare), and on some networks outgoing messages may also be free. Using mobile Internet and WAP while roaming is also fraught with significant costs. Services based on GPRS/EDGE (including MMS) are charged at rates that are much higher than the tariffs of Russian operators: the cost of 1 MB can reach 10-15 dollars. Regular WAP (using a dial-up connection) will be charged as a long-distance or international call using the WAP gateway number, so it makes sense to change the WAP settings by specifying the access number of the guest operator. If you use your phone as a regular dial-up modem, then it is better to purchase an Internet access card from a local provider and access the network through its modem pool.
To check your balance, you can use SMS, USSD or an Internet service if the operator provides these services. In the first case, you can send a message to a special number (or use the SIM menu), and in response you will receive a message about your current balance. In your home zone this service is free, but in roaming you will have to pay for outgoing SMS. In the second case, you need to dial a certain combination of numbers (for example, *102#) and the call button, and information about the balance will be displayed directly on the phone display. In this case, you do not pay for the request, even while roaming. In the same way, you can activate express payment cards, connect and disable additional services.
Pre-paid
Pre-paid (prepaid) - services provided on an advance payment basis. In this case, it is the ability to connect to a mobile operator without concluding a contract. When you arrive in another city or country, you can purchase a SIM card from a local operator, receiving a local number and the ability to make calls at lower rates than with roaming. Usually, you don’t even need to present documents for this (although in Russia they will certainly require a passport). There is no subscription fee, and payment is made using express payment cards, which sometimes have a limited validity period - for example, 7 or 30 days, after which the SIM card can be thrown away, given as a gift to someone, or postponed until the next trip. The lifespan of a blocked SIM card is from 3 to 6 months: during this time it can be renewed. Russian operators also have prepaid: in Bee Line it is Bi+, in MTS it is Jeans, in Megafon it is Light. Tariffs and connection conditions vary in different cities. Typically a starter kit costs $5-10. In Moscow you can buy a set of “Jeans” or “Bi+” for 5 USD. on the account for 50-100 rubles, and during various promotions, SIM cards can be offered at a symbolic price or even free.
It should be noted that Russian operators usually indicate tariffs in conventional units, but these “cu.” are not equal to US dollars. Most often, the tariffs do not take into account VAT (18%), which is written in small letters at the very bottom of the price list or advertising poster. Therefore, all figures must be multiplied by the tax rate. Bee Line adds 1% to the dollar exchange rate, and regional operators can use an internal rate that differs markedly from the official one. However, in the regions tariffs in rubles are often used, including VAT.
It doesn’t always make sense to connect to local operators: sometimes it’s cheaper to use roaming. It is necessary to take into account that if the connection cost is, for example, 20 dollars, there may be only 5 on your account, which will be enough for 2-3 calls home. And if there is a larger amount in the account, then it may not be completely repaid in a few days. If you only need outgoing communication, then it is easier to use a payphone or intercom.
The cost of local outgoing and intercity calls from prepaid is sometimes comparable to the cost of similar calls from a roaming phone. Incoming calls are usually free (abroad) or cost the same as local calls (in Russia). Therefore, receiving calls to a local number is more profitable than to a roaming number, especially since the call is paid not by you, but by the caller. Calls within the network are also beneficial - they are often cheaper than calls within the city/country and are free for the receiving party. So, if you are traveling alone or in a group, periodically separating, you can connect to the same operator and communicate with each other at a price that is not comparable to the cost of a direct call in roaming.
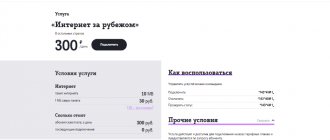
What MTS options are beneficial to connect when traveling around the Russian Federation?
MTS offers its subscribers several additional options that will reduce communication costs when traveling around the country.
Option “Russia is like home everywhere”
This option establishes a single tariff for calls throughout Russia. The subscription fee is 5.2 rubles. per day, calls are charged at 3.2 rubles. in a minute.
To activate the option, send the USSD command *111*528# or use your personal account.
Options “Home package” and “Home package plus”
For MTS package tariff plans, 2 additional options are provided at once:
- "Home package". The subscription fee is charged daily and amounts to 10.5 rubles. per day. Suitable for short trips within the Russian Federation.
- "Home package +". The subscription fee is 104 rubles. per month. Beneficial for trips around the country lasting longer than 10 days.
The meaning of these options is to expand the coverage area of minute and SMS packages to other regions. If your tariff includes only local minutes, connect one of the options and communicate with all of Russia, spending only the package. There will be no overpayments or additional payments. Sending SMS is charged in the same way - they are consumed from the package.
Options are valid throughout Russia. When you return home, be sure to turn them off to avoid unnecessary charges.
To activate the option with daily pricing, send the USSD command *111*743#, to activate the option with monthly payment, dial *111*128#. You can use your personal account.
Tariff plans for which the “Home package”/”Home package +” options are available:
- "Tariffishche";
- "My Unlimited";
- "My Smart";
- "Smart Unlimited";
- "Smart";
- "Smart Mini";
- "Smart Nonstop";
- "X";
- "Smart light";
- “Mobile. BIG";
- "Smart +102014";
- "Smart device" (open version);
- "Smart device 032017";
- “All MTS”/ “My MTS”.
How to activate roaming in Russia
There is no need to activate MTS intranet roaming; it is active for subscribers by default. The only exceptions are some regions where manual connection to the MTS network may be required.
Thus, when located in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug (YNAO), Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug (KhMAO) and the Perm Territory, a mobile phone can automatically connect to the cellular networks of other telecom operators. In this case, charging will be made at national roaming prices. To register in the MTS network, use manual settings in the phone menu. For this you will need:
- Go to your phone settings.
- Find the “available networks” item.
- Update their list.
- Select MTS network.
- Save changes.
In case of difficulties, you can contact customer support by calling our toll-free number 8-800-250-0890
(for calls from numbers of any operators and landline phones) or short number
0890 (for calls from MTS numbers).
What is roaming in simple words?
For those who have little understanding of the complex cellular communications system, we can give a simple definition of the concept of “roaming.” In simple terms, roaming allows an ordinary person to use his own type of communication and his SIM card in any corner of the globe.
And if your network does not function in the area where you are located, then another connection is automatically provided to you under an agreement with yours. Moreover, if there are several cooperating networks in this location, then the network with the best signal is selected.
National roaming MTS in Crimea 2021
Especially many questions arise about MTS roaming in Crimea in 2021. Due to the difficulty of traveling outside the country this season, many Russian citizens are planning to spend their summer holidays in Crimea. The most popular questions from MTS subscribers are: how much does communication cost on the peninsula, how to activate MTS roaming in Crimea, what services and options to choose to save money?
Unfortunately, in Crimea there are still special conditions for the provision of communication services to MTS customers. This is due to the fact that the peninsula is under sanctions, as a result of which the cellular operator does not risk installing its towers in the republic. Therefore, when traveling to Crimea there is still national roaming . This means that MTS subscribers, entering the peninsula, automatically use the services of local telecom operators, remaining on their number.
The cost of minutes, SMS, Internet in Crimea will depend on the MTS tariff and connected additional options.
How to find out if the service is connected
To avoid worries while traveling about whether the option is connected, you need to do one of the following actions:
- Call technical support. The number is listed on the organization’s website, the service is free for all subscribers.
- View information in your personal account.
- Go to the nearest office of the company yourself and ask a specialist about this.
To summarize, it should be noted that without roaming abroad, while traveling or on a business trip, you will not be able to call your loved ones from your number who remain within Russia. For this reason, you should take care of connecting it in advance.
Do I need to activate roaming when traveling to Crimea?
There is no need to activate national roaming in Crimea; this option is enabled by default for MTS subscribers. The exception is when the option was forcibly disabled by the user himself, then it must be enabled again.
There is no MTS network coverage throughout the entire territory of the Crimean Peninsula, so the phone will automatically register in the network of another mobile operator. This could be Win Mobile (K-Telecom), Volna, Krymtelecom or Sevmobile. If you successfully register in the network of one of these operators, the name of the network in whose coverage area you are located will appear on the phone screen instead of the usual “MTS RUS”.
If suddenly registration in the new network does not occur automatically, you should restart the phone (turn it off and on again).
You can choose your own network in the settings. Preference should be given to “WIN” or “25032”; both networks belong to the K-Telecom operator, which has the widest coverage on the peninsula.
To use mobile Internet in Crimea, your phone must allow data transfer while roaming. You can check and allow Internet access in your phone settings according to the following scheme:
- Android : Settings -> Connections -> Mobile networks -> Data roaming (On)
- Apple iOS : Settings -> Cellular -> Data Options -> Data Roaming (On)
Conditions for connecting to the full package
If the country you are going to is not included in the coverage area of the “light” tariff, you need to know how to activate international roaming on MTS. The subscriber must fulfill the following conditions:
- have a positive balance;
- use MTS for at least 6 months. Average communication costs for each month are at least 470 rubles;
- be a user of MTS services for more than a year, while the total communication costs for each month are above 0 rubles.
When all the specified conditions are met and the number is not blocked, the service is activated directly from the phone or in the subscriber’s personal account. Otherwise, the user must contact any operator’s salon. You must have a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation with you. When applying in person, length of service as a network subscriber is not taken into account. The main conditions will be: the presence of an active number and a positive account balance.
How much does MTS communication cost on the Crimean Peninsula?
The cost of mobile communications on the peninsula depends on the subscriber’s tariff and additional options included. On most MTS tariffs, when you are in Crimea, free packages of minutes, messages and traffic are not available, and single base prices are set for calls, sending messages and mobile Internet.
- incoming calls and SMS – free;
- outgoing calls within Russia – 3 rubles. in a minute;
- outgoing SMS within Russia – 3 rubles.
The cost of mobile Internet in Crimea is 1 rub. for every megabyte of traffic.
To save money, you can change the tariff or activate special options for the duration of your trip.
Video
While abroad, the subscriber needs to make calls or write SMS to Russian numbers. The advantages of roaming in this case are obvious: by connecting it, the subscriber will be able to save more than thirty percent on communication services. MTS operators note that when traveling to another country, it is advisable to disable mobile phone functions such as forwarding, receiving voice and MMS messages, mobile Internet, and updating applications. Then money for these services will not be debited. For more information about the benefits of roaming, watch the video:
How to reduce communication costs for MTS in Crimea
To reduce the cost of MTS mobile communication services in national roaming, you can:
- change your tariff plan to a more profitable one;
- connect additional options on your tariff;
- purchase a “local” MTS SIM card without roaming with a special version of the “Super MTS” tariff for Crimea.
Favorable MTS tariffs when located in the Republic of Crimea
On the “Ultra”, “Our Smart” and “Smart TOP” tariffs, no additional options are required. For subscribers of these tariff plans, the roaming conditions in Crimea are the same as for tariffs with active.
Additional options available to MTS subscribers in Crimea
Only a few MTS options are guaranteed to work in Crimea:
- “Russia is like home everywhere”;
- “Home package”, “Home package +”;
- "BIT", "SuperBIT".
Most other services do not work in national roaming. Therefore, before traveling to Crimea, it is advisable to check the connected options on your phone and disable unnecessary ones so as not to pay for them during your vacation.
Option “Russia is like home everywhere”
The additional option “Russia is like home everywhere” is available only on MTS tariffs without a subscription fee. When located in the Republic of Crimea or the city of Sevastopol, all incoming calls for an MTS subscriber become free.
The cost of the option is 5.2 rubles per day. The subscription fee is charged daily, even if the subscriber does not use mobile communications.
Outgoing calls within Russia will cost 3.2 rubles. per minute of conversation.
You can activate/deactivate the service using the USSD command: *111*528#
Options “Home package” and “Home package +”
Both options are intended only for tariffs with a subscription fee and allow you to use packages of minutes, messages and Internet without restrictions. The options differ only in the conditions for charging the subscription fee - daily (10.5 rubles per day) or monthly (104 rubles per month). We have already discussed them in more detail above in the article.
When the option (any) is activated, all incoming calls within the peninsula become free. And for calls and sending SMS, when free packages are exhausted or in their absence, lower prices are set:
- incoming calls and SMS – free;
- outgoing calls within Russia – 2 rubles. in a minute;
- outgoing SMS within Russia – 2 rubles.
You can enable or disable these options using USSD commands:
- “Home package” – *111*743#
- “Home package +” – *111*128#
When activating the “Home Package” option, money for the service is debited only on those days when the subscriber uses mobile communications.
On tariffs with unlimited Internet there are no restrictions on the use of traffic in national roaming. On other tariffs where traffic is limited, after the package is exhausted, additional Internet can be extended automatically in accordance with the terms of the tariff plan or connected by the subscriber independently.
Options “BIT”, “SuperBIT”
These two additional options will be needed to connect Internet packages on tariffs without a monthly fee. They are useful for those who spend a lot of time online, because... significantly reduce the cost of the Internet.
Options are valid throughout Russia, including Crimea, and do not depend on the availability of other options on the tariff plan.
and “SuperBIT” are similar, differing only in the cost and volume of traffic provided. Prices for options:
- “BIT” – 75 MB per day, 200 rubles. per month;
- “SuperBIT” – 3 GB per month, 250 rubles. per month.
If the daily or monthly limit is exceeded, the Internet packages will automatically increase for an additional fee.
You can connect and disconnect “BIT” and “SuperBIT” using your personal account or short USSD commands:
- “BIT” – *111*252*2#
- “SuperBIT” – *111*628#
How to find out whether an option is enabled or not?
If you don’t remember whether you disabled the service or forgot to do it, then use the site. Log in and check the list of active options. It’s even easier to do this on a smartphone if the application is installed - the “Services” button is located in the most visible place.
If you do not use the Internet, call the call center 0890, although you will have to wait for a connection with a consultant; sometimes the waiting time can be up to half an hour.
Or you can go with your passport to the sales office, where they will list you all the connected add-ons.
services. If our article helped you, please like it!