When choosing a smartphone, many users do not pay attention to the characteristics of its modem. All modern devices support 2G GSM and 3G HSPA, and some also support CDMA. 4G LTE support is also present in most models. However, due to the fact that fourth generation networks were deployed at a time when most of the suitable frequencies were occupied by 2G and 3G, operators had to be content with those “windows” that were free. Because of this, frequencies differ in different regions, and when choosing a smartphone, you need to pay attention to the list of supported FDD-LTE and TDD-LTE bands.
FDD-LTE and TDD-LTE are network characteristics that indicate the method of separating the receiving and transmitting channels in the smartphone and at the operator’s base station (communication tower). Separation of counter data flows is necessary so that they do not interfere with each other. What will happen if you transmit and receive information on the same channel can be understood if you imagine a one-lane highway along which cars are moving in both directions. However, you can separate data streams in two different ways.
What is LTE FDD
Many people ask FDD LTE - what is it? This parameter indicates the type of data packet transmission that uses duplex frequency division. If this parameter is used in a smartphone, then the device transmits packets using different frequencies. For example, category BAND 3 (band - frequency), here the frequency of 1710 MHz is used to transmit packets and receive 1810 MHz. If we take a more obvious example, they can serve as a highway divided into two lanes, where traffic is carried out in one direction.
LTE FDD and TDD technology
For your information! If FDD is used, then transmission and reception are carried out in different frequency ranges, so opposing waves do not create additional interference. Thus, signal reception occurs without delay, and the throughput is significantly higher.
At the moment, most operators operating in the country use this technology. This is due to the low cost of maintenance and a more stable signal.
Coverage maps
Typically, an interactive Megafon coverage map can be found on the operator’s website - you will see the network distribution area. Why is this information needed? You can see how stable the Internet is in your region and make a decision about connecting!
The operator is the leader in the number of base stations in Russia - and their number is constantly growing!
- 98,111 LTE Advanced across the country - the largest number among competitors;
- 83 regions of the Russian Federation can use fourth generation communications;
- The speed in 47 regions reaches 300 Mbit per second.
Another truly impressive indicator! If you are interested, it's time to move on to LTE settings .
What is LTE TDD
Frequency ranges LTE Band - what is it?
Also, many are interested in the question, LTE TD - what it is and how it works. The technology implies that the same frequencies are used to transmit and receive data packets for time separation. To eliminate any interference and minimize signal delay, transmission is carried out non-continuously.
In some cases, the phone or basic cellular repeater can only receive or transmit a signal. As an example, consider the BAND 30 standard, which uses the same frequency for receiving and transmitting radio signals at 2600 MHz. To make it more clear, we can again take a specific example - a highway where there is only one lane, but in the morning drivers can only drive in one direction, and in the evening in the other.
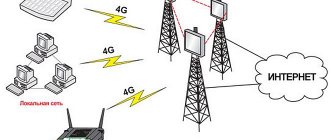
Base station
The TD LTE standard has a number of disadvantages due to the use of only one channel. As a result, signal delay increases and throughput decreases. If the mobile operator uses this particular standard, then different time intervals are set for transmitting and receiving data (5 ms and 10 ms).
Note! Signal delay is most pronounced when a subscriber is communicating with another user via VoLTE.
This LTA standard is used by mobile operators only if there are no frequencies available, but maximum network coverage is required. The standard is applied in the largest cities where there is a relatively high population density. In rural areas, the use of TDD LTE does not make sense, there are not many active subscribers, and because of this, more frequencies can be used to receive and transmit data packets.
Important! Some wireless routers only support BAND 30, 38, and 40 standards.
Tariffs for 4G Internet from MegaFon
We have already figured out what LTE from MegaFon is, where fourth generation networks operate and what equipment we need. It remains to talk about tariff plans - this operator does not have separate tariffs for 4G Internet , so you can take advantage of any other offer:
- “Turn on! Communicate” - 12 GB of Internet for 600 rubles/month;
- “Turn on! Look” - 16 GB of Internet for 950 rubles/month;
- “Turn on! Speak” - 3 GB of Internet for 500 rubles/month;
- “Turn on! Listen” - 6 GB of Internet for 1,400 rubles/month;
- “Turn on! Premium - 20 GB of Internet for 3,000 rubles/month;
- “Turn on! Write” - 2 GB of Internet for 350 rubles/month;
Initially, it may seem that the prices are very high. But do not forget that all tariffs include packages of minutes and SMS - they are aimed at use on mobile phones. It also includes unlimited Internet packages for using social networks, music services, video hosting, as well as popular instant messengers. If minutes and SMS are not needed, we recommend paying attention to the options:
- “Internet XS” - 70 MB for 190 rubles/month, the option works only in Moscow and Moscow Region;
- “Internet S” - 3 GB for 350 rubles/month;
- “Internet M” - 16 GB for 590 rubles/month;
- “Internet L” - 36 GB for 890 rubles/month;
- “Internet XL” - 30 GB during the day and unlimited at night (from 01-00 to 06-59) for 1290 rubles/month.
All options from “Internet S” to “Internet XL” work throughout Russia - stay with LTE from MegaFon wherever you have access to high-speed networks. For tablet PCs there are two separate options:
- “Internet Tablet XS” - 1.5 GB/month for 190 rubles/month;
- “Internet Tablet S” - 4 GB for 400 rubles/month plus mobile TV.
For those who do not have enough traffic, MegaFon offers several options for the “Extend Internet” option, offering traffic volumes from 70 MB to 5 GB.
Rate this article
0
What is the difference between LTE FDD and LTE TDD
What is Smart TV on TV and Wi-Fi - description of functions
The main difference between FDD and TDD is the data transfer speed:
| Communication standard | Data transfer rate | Data reception speed |
| FDD | 50 Mb/sec | 100 Mb/sec |
| TDD | 68 Mb/sec | 17 Mb/sec |
How LTE works
Comparison of characteristics of TDD and FDD technologies:
| Specification | FDD | TDD |
| Radio frequency spectrum used | High spectrum including different frequencies | Low spectrum. This may mean that only one frequency is used |
| Technological complexity | High | Low. Dedicated time required for Downlink and Uplink channels |
| Signal delay | Minimum, up to 1 ms | High signal delay up to 10 ms. Also, this parameter will depend on what range is used to switch between TX-RX channels (reception/transmission) |
| Frequency range | Any frequency can be used. There are no restrictions | Only one frequency can be used, which is used alternately for receiving and transmitting data |
| Download and Upload configurations | Symmetrical data rate is used | The most commonly used is asymmetric packet transmission rate. This is necessary to reduce latency and increase speed over the Downlink channel |
| Dynamic Data Bandwidth Allocation | Not used, since several frequencies are used for Download and Upload | It is implemented for high-quality distribution of data transmission speed between several users in order to reduce signal delay. A simple example: if several users at the same time do not intensively use the traffic bandwidth, then it is distributed to the remaining subscribers, thereby increasing the speed. |
| Spatial coding method (only used to increase traffic bandwidth) | Sophisticated signal encoding to double traffic bandwidth | Lightweight spatial coding |
| Spatial filtering (automatic adjustment of signal strength depending on user location) | Complex | Lung |
Testing the antenna in the field
To test the speed of the antenna, I used the Speedtest.net service. To compare the speed, I took a modem from Megafon with me and tested it with the same 4G SIM card.
We decided to test the antenna in the field conditions for which it was, in fact, intended. Since I have neither a dacha nor a country house, we simply went out into nature - into the forest not far from the city (about 12 km).
In the meadow
We assembled it according to the instructions included in the kit: we connected the antenna to the POE adapter, the adapter to the laptop and connected it to the car’s network via a converter.
Antenna connection
Connected and ready to go
It must be said right away that we tested in more than one place - somewhere the antenna worked better, somewhere worse. In the original location, where the modem completely refused to pick up a 4G signal, the antenna gave an incoming speed of 6.21 Mbit/s.
Looking for a signal
Speedtest results
The fishing was best near the car, although due to the long cable we moved around the entire clearing, trying to catch the best signal. The most successful indicator in this area is 8.62 Mbit/s (stopped on a hill).
Speedtest results in the second location
The next place was closer to the city, about 5 km, in a field.
We catch a signal in the field
Here the modem from Megafon started working. It returned 0.05 Mbps (not to mention that we could barely wait for it to open the speed test at all).
Speed test with modem
With the antenna, mobile Internet from Megafon soared to 11.95 Mbit/s. In principle, these were the best results that were achieved.
General impression
If you use a 3G/4G antenna outside the city, where the Internet often disappears altogether, the performance is very different from the same modem (as can be seen in the screenshots above).
In a forest clearing 12 km from the city, we got the speed with which we can use the Internet without the risk of breaking the computer from rage.
In principle, if instead of a person who wanders through the field and forest clearings, raising the antenna above his head, there was a master who will install the antenna on the roof of the dacha, the speed would be even faster.
But, as I said above, to connect an antenna and get your legitimate 5-10 Mbit/s even on 3G, you don’t need any knowledge or skills.
PS HiTE also produces more powerful 4G LTE antennas, but we chose the HYBRID model for testing for its versatility and ease of setup. published by econet.ru
Join us on Odnoklassniki
At what frequencies do these technologies operate?
What is a Wi-Fi router and how does it work
LTE technology operates on different frequency bands (BAND, or band). For FDD there are several bands: 1, 3, 7, 20, in turn for TDD - 33, 38, 40 and 44. In Russia, mobile operators use the following:
| Range | 1800 MHz | 2500 MHz | 800 MHz | 2600 MHz |
| BAND | 3 | 7 | 20 | 38/40 |
| Technology | FDD | FDD | FDD | TDD |
For your information! The LTE FD 800 MHz standard is used by mobile operators Megafon, Beeline and Tele2. This distribution is relevant for large cities where large network coverage is required. Almost all companies use the BAND 20 range.
Some users ask which is better: LTE 1800 MHz or LTE 2600 MHz. Thanks to the first, the signal penetrates better through various obstacles, such as concrete or steel walls. In turn, thanks to the second reception, the signal reception is better and more stable; there is also no need to use a large number of base stations, since their range reaches up to 20 km.
Frequency range
What is frequency aggregation
Frequency aggregation is the aggregation of spectrum. Thus, the signal is transmitted at several frequencies at once, and as a result there is virtually no delay and the speed of receiving and transmitting traffic packets increases. At the moment, this technology is used by the transitional generation 4G, which is referred to as 4G+ or 4.5G.
Note! Frequency aggregation allows devices to connect to multiple channels and combine them to improve signal quality and Internet connection speed.
Cat 1, cat 2, cat 3, cat 4… cat 12, cat 16 and others
Many people ask what CAT 4 LTE is. Today, most smartphone models use CAT4, which shows the maximum data transfer speed. This category allows you to achieve speeds of more than 50 Mb/sec, but several conditions must be met:
- be a few meters from the repeater;
- No third party subscribers should be connected to this point;
- the base station uses powerful equipment;
- The repeater uses an optical (fiber) connection to the network center.
In addition to LTE CAT 4, there are several more categories:
| Category | Transfer speed in Mb/sec |
| CAT4 | 150 |
| CAT6 | 300 |
| CAT9 | 450 |
| CAT12 | 600 |
| CAT16 | 980 |
Important! The CAT 4 LTE category shows information about what data rate the mobile phone supports.
How to tell if a smartphone supports 4G: buying tips
Almost all modern smartphones and tablets are equipped with a module to support LTE networks. To check the ranges, you need to carefully examine the packaging box of the new device. Manufacturers always leave information about the networks and frequencies for which the device is manufactured. Russian LTE frequencies must be indicated on the packaging, otherwise you should refrain from purchasing.
To buy a proven device, you need to adhere to the following points:
- Purchase gadgets from authorized dealers or large electronics stores.
- Check the information on the packaging.
- Ask the manager to insert a SIM card and make sure there is a 4G icon on the display.
In Russia, most often the main frequency is LTE band 20. If the device does not have a module that is configured for this frequency, the Internet speed can be significantly reduced.
Advantages and disadvantages of these technologies
Advantages and disadvantages of FDD:
| pros | Minuses |
| Most mobile operators use this technology | The reception and transmission channels are close together, so a guard band is needed |
| Splitting the signal allows you to improve Internet speed | Installation of filters to isolate frequencies from each other. Close proximity of channels can cause interference and reduced throughput |
| Significantly higher throughput | Due to the fact that transmission and reception are carried out on different channels, the speed may not be constant. |
| Radio waves can travel up to 10 km |
Data transfer rate depending on frequency aggregation
Using FDD technology reduces latency and increases Internet connection speed. To get a better and more stable signal, you need to purchase a device that supports BAND 3 and 7, since they work with FDD. When using TDD, you may experience inconsistent Internet connection speeds and an unstable signal.
Premise
Released in 2008, LTE is technically referred to as a 3GPP technology and is designed to work with mobile computing devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers. At the time of publication, LTE technology is available on a select number of phones that offer 4G network access. Wi-Fi technology came to market in 1999 with the release of the 802.11b standard and was intended to provide wireless networking functionality for computers and mobile devices. Unlike LTE technology, Wi-Fi standards require a router to provide a wireless network.